Alcohols ,phenols and ethers
Reasoning based questions
Q.1.The boiling point of alcohols increases with increase in the number of carbon atoms why ?
Ans As mass increases van der Waals force between molecules increases hence boiling point increases.
Q.2.Boiling point of alcohols is higher than hydrocarbons, ethers, haloalkanes of comparable molecular masses why?
Ans.Higher boiling point of alcohols is due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding in them which is not present in ethers, haloalkanes, haloarenes and hydrocarbons.
Q.3.Alcohols are soluble in water why?
Ans.Solubility of alcohols in water is due to their ability to form hydrogen bond with water molecules.
Q.4.Solubility of alcohols decreases with increase in number of carbon atoms why?
Ans.It is due to increasing hydrophobic alkyl part in alcohols.
Q.5.Arrange the following sets of compounds in order of their increasing boiling points:
(a) Pentan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, ethanol, propan-1-ol, methanol.
(b) Pentan-1-ol, n-butane, pentanal, ethoxyethane.
Ans (a) Methanol < ethanol < propan-1-ol < butan-2-ol < butan-1-ol < pentan-1-ol
(b) n-Butane, ethoxyethane, pentanal and pentan-1-ol
n-butane has dispersion force ether, pentanal have dipole-dipole attraction and alcohol has H-bonding between their molecules.
Q.6.Give a reaction which proves alcohols are acidic in nature.
Ans. R-OH + Na → R-ONa + H2 . Evolution of H2 gas with metals proves that alcohols are acidic in nature.
Q.7.Give two reactions which prove phenol is acidic in nature.
Ans.
C6H5OH + Na → C6H5ONa + H2
C6H5OH + NaOH → C6H5ONa + H2O
Q.8.Give a reaction which shows alcohols are Bronsted acid.
Ans.
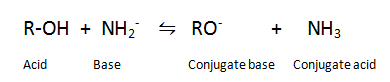
Ans. Alcohols can donate a proton to a stronger base.
Q.9.Give a reaction which shows alcohols are weaker acid than water.
Ans.
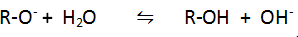
Q.10.Arrange primary ,secondary and tertiary alcohol in decreasing order of their acidic strength.
Ans.
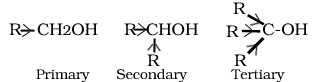
An electron releasing alkyl group increases electron density on oxygen tending to decrease the polarity of O-H bond. This decreases the acid strength.
Q.11.Give a reaction which shows alcohols act as Bronsted bases.
Ans It is due to the presence of unshared electron pairs on oxygen, which makes them proton acceptors.
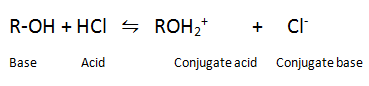
Q.12. Phenol is stronger acids than alcohols and water.
Ans
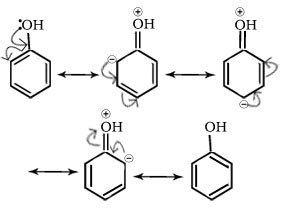
In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalized,hence phenoxide ion is more stable than alkoxide ion.Thus phenol is more acidic than alcohol.
Q.13.Arrange o- Nitrophenol p-Nitrophenol m-Nitrophenol o-cresol,m-cresol,p-cresol ,phenol and ethanol in decreasing order of acidic strength.
Ans. p-Nitrophenol ˃ o- Nitrophenol ˃ m-Nitrophenol ˃phenol ˃ m-cresol ˃o-cresol ˃p-cresol ˃ethanol
Explanation:1
The presence of electron withdrawing groups such as nitro group, enhances the acidic strength of phenol and releasing groups, such as alkyl groups decreases the acidic strength.
Explanation:2
Phenoxide ion is more stable when withdrawing group is present on ortho and para positions It is due to the effective delocalisation of negative charge in phenoxide ion.
Explanation:3
Phenoxide ion is less stable when releasing group is present on ortho and para position.
Q.14.Arrange following compounds in the order of their acidic strength:
Propan-1-ol, 2,4,6-trinitrophenol, 3-nitrophenol, 3,5-dinitrophenol, phenol, 4-methylphenol.
Ans. Propan-1-ol < 4-methylphenol < phenol < 3-nitrophenol <3,5-dinitrophenol <2,4,6-trinitrophenol
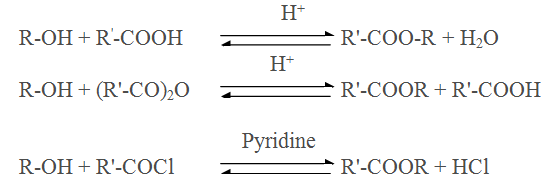
Q.15.During esterification between carboxylic acid and acid chloride pyridine is mixed with solution why ?
Ans Since esterification is reversible reaction hence the reaction with acid chloride is carried out in the presence of a base (pyridine) to neutralise HCl which is formed during the reaction.
Q.16.During esterification between carboxylic acid and alcohol water is removed as
soon as it is formed why?
Ans. Since esterification is reversible reaction hence water is removed as soon as it is formed.
Q.17.Arrange the reactivity of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols towards dehydration in decreasing order.
Ans Tertiary > Secondary > Primary. it is due to decreasing order of intermediate carbocation in following order
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary (+I effect decreases)
Q.18.–OH present at benzene ring in phenol is activating group and ortho and para directing why?

Ans. It is due to +R effect of –OH group electron density is high at ortho and para position.
Q.19 .Which is steam volatile in o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol .
Ans.O-nitrophenol is steam volatile due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding while p-nitrophenol is less volatile due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding which causes the association of molecules.
Q.20.Formation of ethers from dehydration of alcohol is suitable having primary alkyl groups only why?
Ans.The reaction follows SN1 pathway when the alcohol is secondary or tertiary and elimination competes over substitution and alkenes are easily formed.
Q.21. In the formation of ethers from Williamson synthesis better results are obtained if the alkyl halide is primary.
Ans.In case of secondary and tertiary alkyl halides, elimination competes over substitution. If a tertiary alkyl halide is used, an alkene is the only reaction product and no ether is formed.
Q.22.Compare boiling point between alcohols and ethers having comparable mass.
Ans Since alcohol molecules are joined with each other by H-bonding and ethers have weak dipole -dipole interactions hence alcohols have higher boiling point than ethers.
Q.23. Ethers are soluble in water why?
Ans Oxygen of ether can also form hydrogen bonds with water molecule.
Q.24.Arrange reactivity of different hydrogen halide with ether in decreasing order.
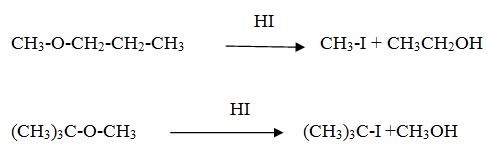
Ans The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides is HI > HBr > HCl
Q.26.The alkoxy group (-OR) is ortho ,para directing and activates the aromatic ring towards electrophilic substitution why.
Ans
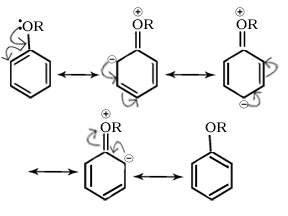
Ans. It is due to +R effect of –OR group electron density is high at ortho and para positions.
Distinguish reactions
Distinguish between ethanol and phenol (Iodoform test)
Ethanol gives Iodoform test.
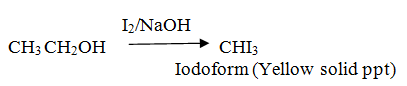
Phenol doesn’t give Iodoform test.
Distinguish reaction between ethanol and propanol(Iodoform test)
Ethanol gives Iodoform Test.
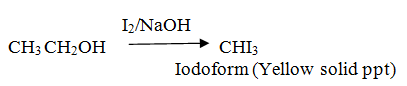
Propanol gives no Iodoform test.
Distinguish reaction between propanol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol(Lucas test)
Tertiary alcohol (2-methylpropan-2-ol) reacts with Lucas reagent (HCl+ZnCl2) immediately and produce haloalkane with turbidity. Primary alcohol (Propanol) does not produce turbidity at room temperature.
Name reactions
Kolbe’s reaction

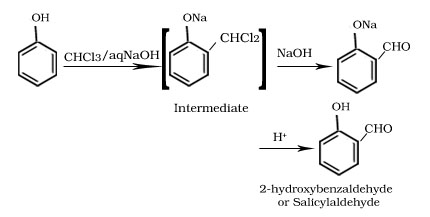
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Williamson synthesis
R-X + R-ONa → R-O-R + NaX
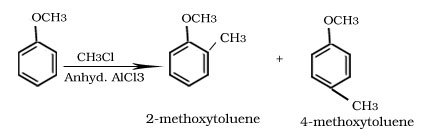
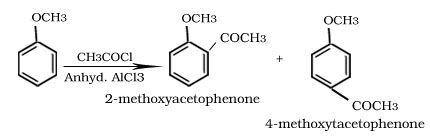
Friedel -Crafts alkylation and acylation reaction of anisole
Nitration of anisole

Halogenation of anisole

Mechanism
Ethene to ethanol
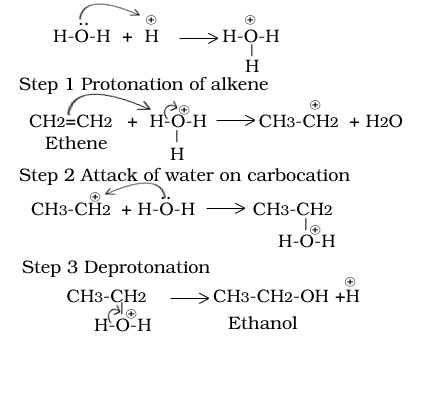
Ethanol to ethene
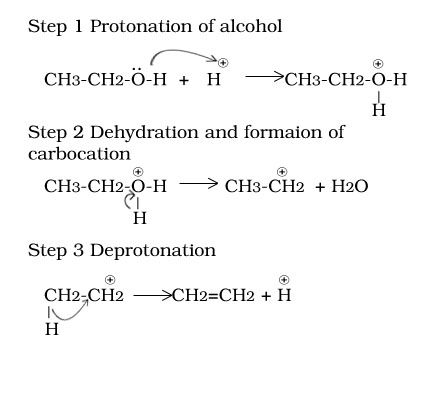
Ethanol to ether
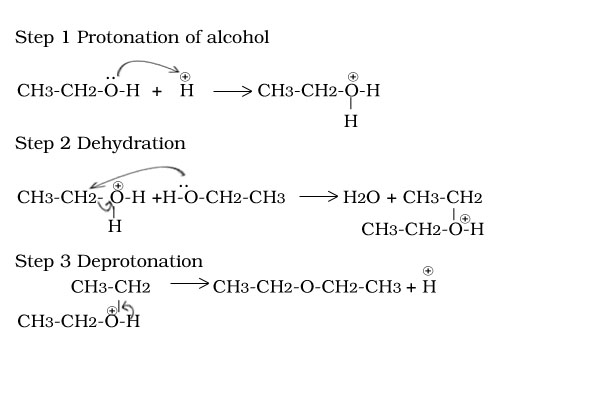
Reaction of ethoxy ethane with HI
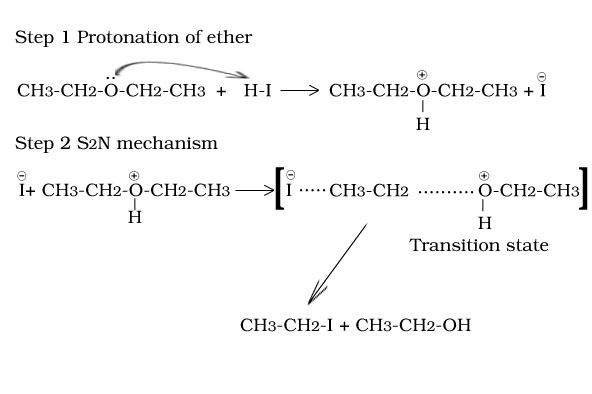
Reaction of tertiary butyl methyl ether with HI
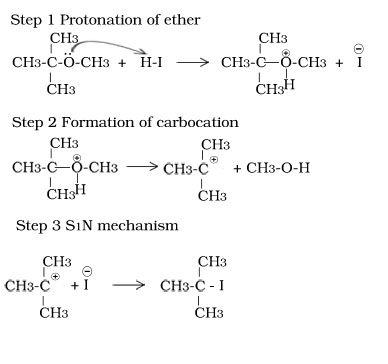
Other reactions
Markonikov hydration of alkene
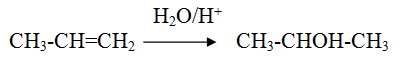
Hydroboration -oxidation reaction of alkene
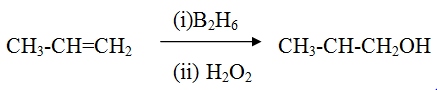
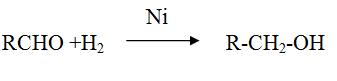
Reduction of aldehyde and ketone
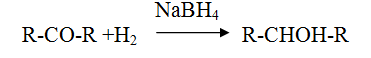
Reduction of Carboxylic acid
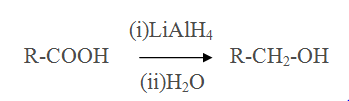
Reaction of Grignard reagent with methanal,other aldehydes and ketones
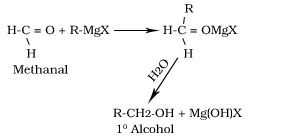

Formation of phenol from chlorobenzene

Formation of phenol from benzene and oleum

Formation of phenol from Cumene
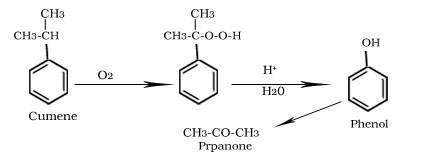
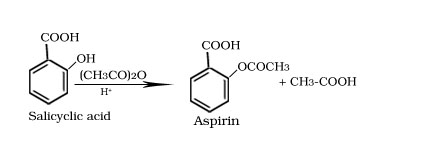
Formation of aspirin from salicyclic acid
Esterification of alcohol using carboxylic acid,anhydride,acid halide
Acid catalysed Dehydration of primary alcohol, Secondary alcohol,Tertiary alcohol
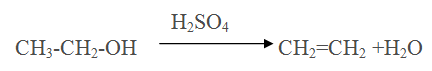
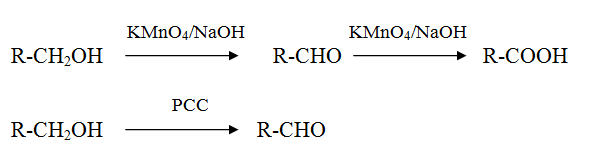
Oxidation of alcohol
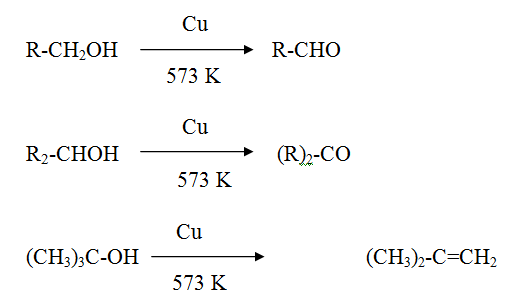
Reaction of alcohol with hot copper
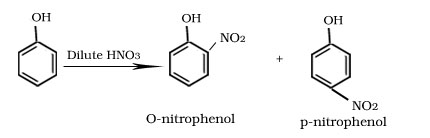
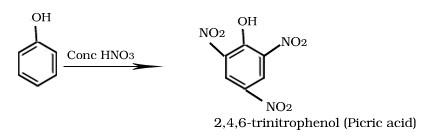
Nitration of phenol
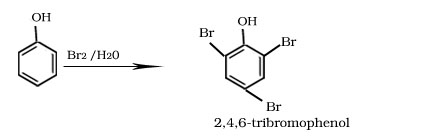
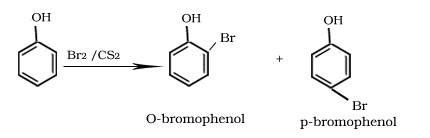
Bromination of phenol
Reaction of phenol with zinc dust

Oxidation of phenol

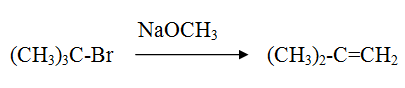
Reaction of tertiary alkyl halide with sodium alkoxide
Reaction of ethers with HX