Chemical kinetics
Define rate of reaction.
Change in concentration of reactant per unit time is called rate of reaction

What is the unit of rate of reaction.
Mol L-1 S-1
Define average rate of reaction.
Average rate of reaction is always define in particular interval.
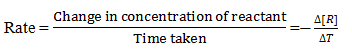
Define Instantaneous rate of reaction.
Rate of reaction at particular instant is called instantaneous rate of reaction.
Express the rate of reaction in terms of each reactant and each products.
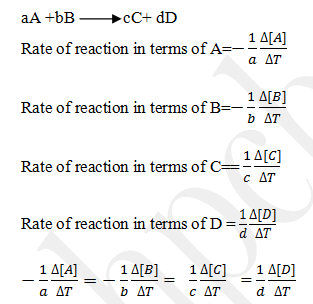
Write the equation for rate of disappearance of A and B and rate of formation/production/appearance of C and D.
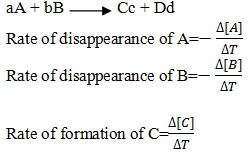
Define rate law/Differential Rate Laws
According to rate law; rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of reactants raise to the power equal to order of reaction in terms of that reactant.
aA+Bb= Products
Rate=K[A]l[B]m
Where K= constant called rate constant or specific rate constant.
l=order of reaction in terms of A.
m=order of reaction in terms of B.
What is the unit of rate constant.
Unit of K=mol1-nLn-1S-1
Where n=Order of reaction.
For Zero order reaction= mol1L-1S-1
For first order reaction= S-1
For second order reaction= mol-1L1S-1
Define Order of reaction.
Sum of the power of concentration terms in rate law equation is called order of reaction.
aA+Bb=
Rate=K[A]l[B]m
For example order of reaction for this reaction is- (l+m)
Define Rate Constant K.
The rate constant of a reaction is defined as rate of reaction when concentration of reactants are taken unity.
Rate=K[A]l[B]m
let [A]=1M and [B]=1M
Rate=K
What are the features of order of reaction.
1.Order of reaction may be +ve ,-ve or fraction.
2.Order of the reaction is pure experimental quantity it cannot be determined by just looking the reaction.
3.If a reaction occurs in more than one step slowest step is rate determining step.
Define Molecularity of the reaction.
Total no. of reactants molecules for formation of product is called molecularity of reaction.
What are the features of molecularity.
1.Molecularity never be fraction ,negative it is only +ve integer.
2.Molecularity can be determined by just looking the reaction.
3.If a reaction occurs in more than one step each step has its own molecularity.
4.The molecularity of a reaction can not be greater than three because more than three molecules may not mutually collide each other to have an effective collision.
Define pseudo first order reaction with two examples.
Pseudo first order reaction is actually of higher order reaction but can be approximated or appears to be pseudo first order reactions.
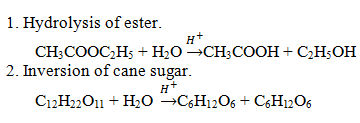
Concentration of water can be approximated as consantt as is concentration does not change a lot during the reaction.
Derive integrated rate equation for zero order reactions.

Give some examples of zero order reaction.
1.The decomposition of gaseous ammonia on a hot platinum surface is a zero order reaction at high pressure.
2.The thermal decomposition of HI on gold surface .
Define Half life period .
The time in which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to one half of its initial concentration It is represented as t1/2.
Derive half life period for zero order reaction.
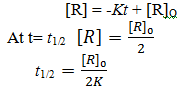
It is to be noted that half life period depends on the initial concentration of the reaction.
Derive integrated rate equation for first order reactions.
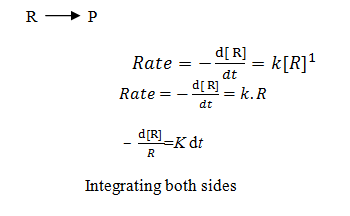

Derive half life period for first order reaction.
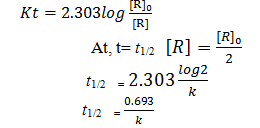
It is to be noted that half life period is independent from initial concentration.
How does the rate constant change with per 10o rise of temperature.
The rate constant is nearly doubled for a chemical reaction with rise in temperature by 10o
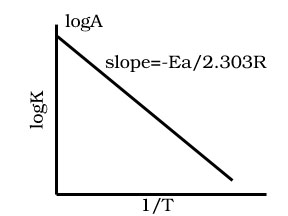
How does the rate constant change with temperature according to Arrhenius equation.
K = A e –Ea /RT
where A is the Arrhenius factor or the frequency factor or pre-exponential factor.
Ea is activation energy.
R is gas constant.
Taking natural logarithm of both sides
ln K = ln A –Ea/RT

Define activation energy(Ea)
Activation energy, in chemistry, the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms or molecules to a condition in which they can undergo chemical transformation
Define threshold energy.
It is the minimum amount of energy which the reactant molecules must possess for the effective collision in forming the products
Define most probable kinetic energy.
The energy possessed by maximum number of molecules called most probable kinetic energy.
Define Collision frequency.
The number of collisions per second per unit volume of the reaction mixture is known as collision frequency (Z).
Define effective collisions.
The collisions in which molecules collide with sufficient kinetic energy called threshold energy and proper orientation, so that they can form products are called effective collisions.
Draw graph for zero order reaction between concentration [R] and time t.
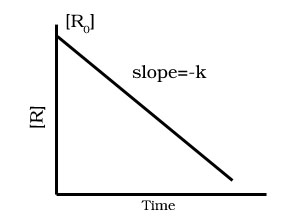
Draw graph for first order reaction between concentration log [R] and time t

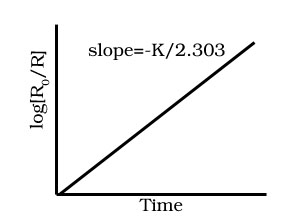
Draw graph for first order reaction between concentration log [Ro]/[R] and time t.
Draw graph for Arrhenius equation between concentration logK and time 1/T.