Solution
Define Binary solution.
The homogeneous mixture of two components in which one component is called solute and another component is called solvent.
Types of solution on the basis of physical state of solvent and solute.
Nine types of solution.
Solid+Solid.
Solid+Liquid.
Solid+Gas
Liquid+Solid
Liquid+Liquid
Liquid+Gas
Gas+Solid
Gas+Liquid
Gas+Gas
Define the term concentration.
Amount of the solute present in given amount of solvent is called concentration.
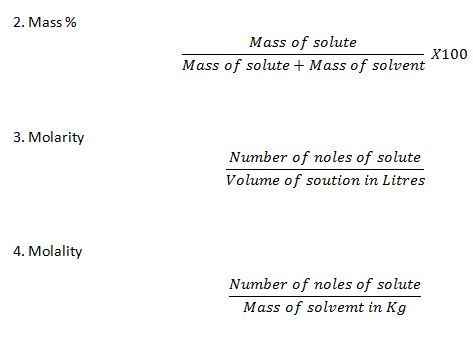
Different types of concentration terms.
1.Molarity.
2.Molality
3.Mole fraction.
4.Mass percentage
5.Concentration in ppm.
Molarity-Number of moles of solute present in one litre of solution.
M=n/V
Where n= Number of moles of solute and V=Volume of solution in liter.
Molality= Number of moles of solute present in one Kg of solvent.
m=n/w
where n= Number of moles of solute and w=mass of solvent in Kg.
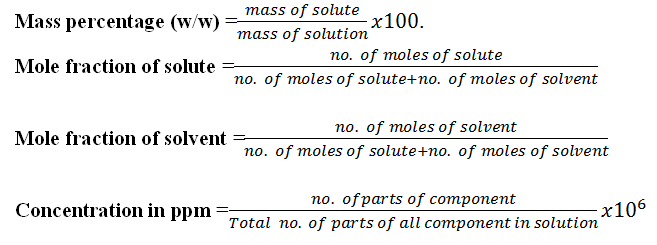
Define the term solubility.
The maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved into given amount of solvent at given temperature is called solubility of that solute.
Factors which effect the solubility.
1.Nature of the solvent and solute
2.Temperature.
3.Pressure.
Define the term dissolution.
The process of dissolving solid in liquid due to which concentration of solid increases in solution is called dissolution.
Define the term crystallization.
The process in which solid solute particles collide with each other and get separated out of solution is called crystallization.
Define the term saturated solution.
When rate of dissolution is equal to the rate of crystallization the solution is called saturated solution. In this solution no more solute can be dissolved at given temperature and pressure.
Define the term unsaturated solution.
In this solution more solute can be dissolved at same temperature and pressure.
Conditions of solubility of particular substance in particular solvent.
Like dissolves in like that is a polar solute can dissolved in polar solvent and non polar substance can be dissolved in nonpolar solvent.
Explain the effect of pressure on solubility of solid in a liquid.
Effect of pressure on solubility of solid in liquid is not significant because compressibility of solid and liquid is very low.
Explain the effect of temperature on solubility of solid in a liquid.
Solubility of solid in liquid is reversible process. If dissolution process is endothermic (Δsol H > 0), the solubility should increase with rise in temperature and if it is exothermic (Δsol H < 0) the solubility should decrease according to Le Chateliers Principle.
Explain the effect of pressure on solubility of gas in a liquid.
Solubility of gas in a liquid increases on increasing pressure. Since dissolution of gas in liquid is reversible process so increasing pressure more of gas must be dissolved in liquid to decrease the process so that equilibrium should maintained.
Explain the effect of temperature on solubility of gas in a liquid.
Dissolution process involves dynamic equilibrium and thus must follow Le Chatelier’s principle. As dissolution is an exothermic process, the solubility should decrease with increase of temperature.
Explain Henry’s law and its applications.
The amount of solute that can be dissolved in given amount of solvent at given temperature is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid
p = KH x
KH is the Henry’s law constant.
X=mole fraction
Applications.
1.When CO2 is packed in soda water or In soft drinks it is packed under high pressure.
2.People suffer from a medical condition called anoxia at high altitude.
It is due to pressure of air at high altitude is low so solubility of oxygen in blood becomes low.
3. Scuba divers suffer from a medical condition called bends when they come out from deep sea water to the surface. It is due to when they come out towards surface pressure gradually decreases and bubble of nitrogen is formed in blood.
Why aquatic species are more comfortable in cold waters rather than in warm waters.
Solubillty of gas increases with decrease in temperature so that aquatic species are more comfortable in cold waters rather than in warm waters.
Define vapour pressure.
In a closed container when rate of evaporation is equal to the rate of condensation the pressure of a vapor above its liquid is called vapor pressure.
Which has higher vapour pressure in solvent and solution if a non volatile solute is added to the solvent.
Vapour pressure of solvent is higher than the vapor pressure of solution because no. of particles of volatile solvent decreases at the surface of liquid in case of solution.
Expain Raoult’s law.
For any solution the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction.
Or
When non volatile solute (like solid solute) is added to the solvent vapour pressure of solution is directly proportional to the mole fraction of solvent.
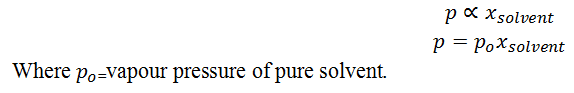
What is colligative properties.
The properties of solution which don’t depend on the nature of the solute but depends on the amount of solute is called colligative properties.
Types of colligative properties.
1.Relative lowering of vapour pressure .
2.Elevation of boiling point.
3.Depression of freezing point.
4.Osmotic pressure.
Derive the equation for relative lowering of vapor pressure when non volatile solute is added to the volatile solvent.
According to Raoult’ law

Derive an equation for the calculation of total vapour pressure when two components in solution are volatile.
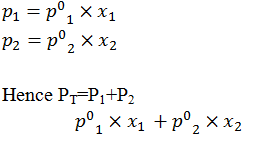
Why boiling point of solution is higher than that of solvent when non volatile solute is added to the volatile solvent.
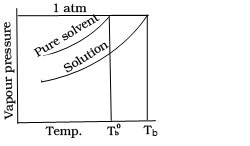
Since vapour pressure of solution is lower than that of solvent hence vapour pressure of solution will be equal to1atm at higher temperature.
Derive an equation for determination of elevation of boiling point when non volatile solute is added to the volatile solvent.

Why freezing point of solution is lower than that of solvent when non volatile solute is added to the volatile solvent.
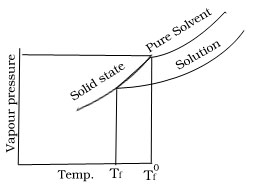
Since vapour pressure of solution is lower than that of solvent hence vapour pressure of solution will be equal to vapour pressure of its solid state at lower temperature.
Derive an equation for determination of depression in freezing point when non volatile solute is added to the volatile solvent.
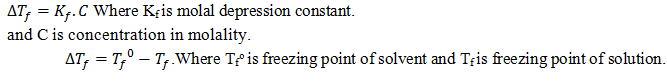
Define osmosis.
The spontaneous phenomena of flowing solvent molecules from lower concentration solution to higher concentration solution is called osmosis.
What is the reason of osmosis.
Since vapor pressure of lower concentration is higher than higher concentration side.
Define osmotic pressure.
The extra pressure which is applied on the higher concentration solution side to prevent osmosis is called osmotic pressure.
How can we calculate osmotic pressure.

A raw mango is placed in concentrated salt solution, it shrivels into pickle why.
Raw mango loses water via osmosis.
Why wilted flowers revive when placed in fresh water?
Osmosis occurs due to vapor pressure difference and water molecules flow from fresh water to flower.
Carrot that has become limp because of water loss into the atmosphere can be placed into the water making it firm once again.
Osmosis occurs due to vapor pressure difference and water molecules flow from fresh water to carrot.
Define isotonic solution.
Two solution having same osmotic pressure at constant temperature is called isotonic solution.
Explain Hypertonic and Hypotonic solution.
Two solutions which are separated by SPM in which one solution has osmotic pressure lower than the other, the lower osmotic pressure solution is called hypotonic solution and higher osmotic pressure solution is called hypertonic solution,
Why sodium chloride solution, called normal saline solution having concentration of 0.9% (mass/mass) is safe to inject intravenously.
The osmotic pressure of the fluid inside the blood cell is equal to 0.9% (mass/mass)
When blood cells placed in a solution containing more than 0.9% (mass/volume) sodium chloride, it would shrink why?
Because water molecules flow out from blood cells to sodium chloride solution via osmosis .
When blood cells placed in a solution containing lower than 0.9% (mass/volume) sodium chloride, it would swell why?
Because water molecules get inside to blood cells from sodium chloride solution via osmosis.
Explain reverse osmosis and application of it.
When extra pressure which is applied to the higher concentration solution is higher than the osmotic pressur the process is reversed. Now water molecules passes from higher concentration solution to lower concentration this process is called reverse osmosis.
We can apply reverse osmosis to reduce the salt level from salty water.
Define ideal and non ideal solution.
Ideal solution–Solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
Solutions which don’t obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known non ideal solutions.
What are the features of ideal solution?
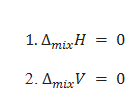
3.If the two components of solution are A and B than intermolecular force of attraction between A-B is nearly equal to the A-A and B-B.
4.Examples.n-hexane and n-heptane, bromoethane and chloroethne benzene and toluene .
Types of non ideal solution.
Non Ideal solution have two types.
1.Non Ideal solution having +ve deviation.
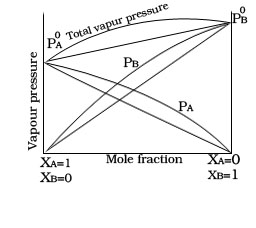
3 .If the two components of solution is A and B than intermolecular force of attraction between A-B is lesser than the A-A and B-B.
4. Example.Mixture of alcohol and acetone
1.Non Ideal solution having -ve deviation
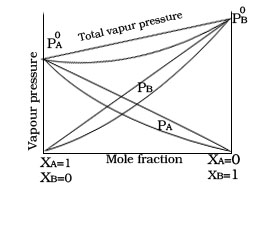
3. If the two components of solution is A and B than intermolecular force of attraction between A-B is higher than the A-A and B-B.
4. Example.Mixture of chloroform and acetone.
Define Azeotropic mixture.
The mixture of the two components which boil at same temperature. These type of mixture can’t be separated by fractional distillation.
Types of azeotropic mixture.
a.Maximum boiling azeotropic mixture.
Mixture of the two components which boilng point is higher than the either of the two components. This type of mixture shows large –ve deviations from Raoult’s law. Example. 68% nitric acid and 32% water by mass.
b.Minimum boiling azeotropic mixture.
Mixture of the two components which boilng point is lower than the either of the two components.This type of mixture shows large +ve deviations from Raoult’s law.
Example 95% by volume of ethanol in water.
What do you mean by Van’t Hoff factor.
Factor which makes experimental and theoretical value of colligative property equal.