States of matter
Intermolecular forces of attraction.
The forces of attraction and repulsion between constituent particles of matter a molecule or atom is called intermolecular force of attraction.
Different types of attractive intermolecular forces of attraction (van der Waals forces).
van der Waals forces are of three types.
(i)London forces/dispersion force-Between non polar molecules.
(ii)Dipole-dipole forces- Between polar molecules.
(iii)Dipole-induced dipole forces- Between non polar and polar molecules.
H-bonding-A particular type of dipole-dipole interaction acts between hydrogen of one molecule and F or O or N of other molecule.
What is thermal energy.
Energy of the substance arises due to motion of it constituent atoms or molecules.
Thermal energy of substance in their different physical states decreases in following order.
Gas>Liquid>Solid
Define Boyle’s Law.
At constant temperature, the pressure of a given mass of gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
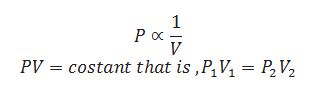
Define isotherm.
Each curve corresponds to a different constant temperature in pressure, p vs. Volume, v is called isotherm.
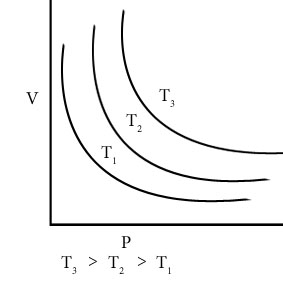
Draw Graph of pressure, p vs.1/V of a gas at different constant temperatures.
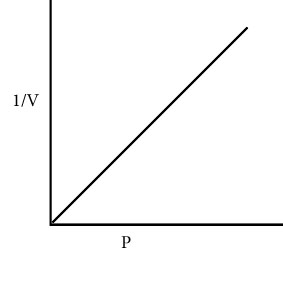
Define Charle’s law.
At constant pressure the volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
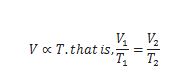
Draw Volume vs. Temperature graph at constant pressure.
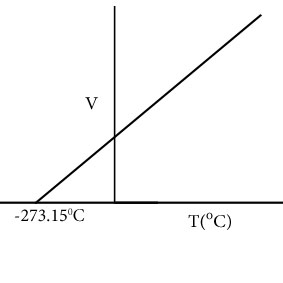
Define isobar.
Each line in Volume vs Temperature graph at constant pressure is called isobar.
Define absolute zero.
Hypothetical temperature at which volume of gases are considered zero is called absolute zero.This temperature is -273.15oC.
Explain Gay Lussac- Law.
At constant volume, pressure of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature.
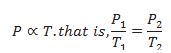
Define isochore.
Each line in Pressure vs. Temperature graph at constant volume is called isochore.
Define Avogadro Law.
Equal volumes of all gases under the same temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules.
What do you mean by STP.
STP means standard temperature and pressure. Standard temperature is 273.15 K (0oC) and standard pressure is 1 bar .At STP molar volume of an ideal gas is 22.7 L mol–1.
Define ideal gas.
Gas which obeys all types of gas laws Boyle’s law, Charles’ law and Avogadro law strictly is called an ideal gas.
What is ideal gas equation.
Combination of four gas laws gives ideal gas equation.

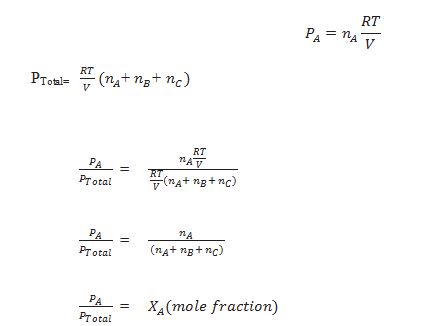
Define partial pressure.
The pressure exerted by the individual gas in mixture of gases is called partial pressure.
Define Dalton’s Law of partial pressure.
The total pressure exerted by the mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial
pressures of individual gases.
PTotal = PA+PB+PC……………
Let at the temperature T, three gases A,B and C enclosed in the volume V, exert partial pressure pA, pB and pC respectively. then,
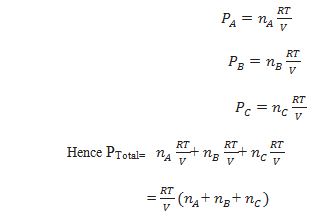
Waht is the relation between partial pressure mole fraction, total pressure and partial pressure.
Define aqueous tension.
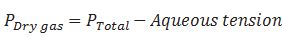
Pressure exerted by saturated water vapour is called aqueous tension.
What is the different assumptions or postulates of the kinetic molecular theory of gases.
(i)The volume of the molecules is negligible in comparison to the empty space between them.
(ii) There is no force of attraction between the particles of a gas at ordinary temperature and pressure.
(iii) Particles of a gas are always in constant and random motion in straight lines
(iv)Pressure exerted is due to collision of the particles with the walls of the container
(v) Collisions of gas molecules are perfectly elastic thus the total energy of molecules before and after the collision remains constant.
(vi)The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
Which assumption of kinetic theory explains the great compressibility of gases.
The volume of the molecules is negligible in comparison to the empty space between them.
Which assumption of kinetic theory explains that gases expand and occupy all the space available to them.
There is no force of attraction between the particles of a gas at ordinary temperature and pressure.
Why do gases deviate from the ideal behaviour?
It is due to following reasons.
(i) The volume of the molecules is negligible in comparison to the empty space between them.
(ii) There is no force of attraction between the particles of a gas at ordinary temperature and pressure.
What are the conditions under which gases deviate from ideality?
Gases deviate from ideal behaviour when compressibility factor Z>1or Z<1.This is possible at high pressure and low temperature when molecules of gases are very close to each other and intermolecular forces become significant.
What are the conditions under which gases follow ideal gas equation and very close to ideality?
Gases behave as ideal gas when compressibility factor Z=1.This is possible at very low pressure and high temperature when molecules of gases are very far to each other and intermolecular forces are negligible.
What are the real gas/van der Waals equation.

What is the significance of ‘a’ and ‘ b’ in real gas equation.?
’a’ is measure of magnitude of attractive forces between the molecules .Higher the value of ‘a ‘easier’ the liquefaction. ‘b’ is effective size of molecules, higher the value of ‘b’ smaller is the compressible volume.
What is the unit of van der Waals ‘a’ and ‘b’.
Unit of a=L2 mol-2atm.
Unit of b=Lmol-1
What is compressibility factor Z.
Z determine the deviation of gas from ideal behaviour.
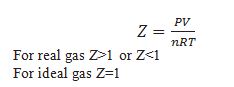
Define Boyle point/ Boyle temperature.
The temperature at which a real gas obeys ideal gas law over an appreciable range of pressure is called Boyle temperature or Boyle point.
How can compressibility factor is determined id VReal and VIdeal are given.

Define critical temperature(Tc) critical pressure(Pc) ,critical volume(Vc).
Critical temperature(Tc)- Highest temperature at which gases can be liquefied by increasing pressure above this temperature gases can’t be liquefied.
Critical pressure(Pc)– Pressure of one mole of gas at critical temperature is called critical pressure (pC).
Critical volume (VC) -Volume of one mole of the gas at critical temperature is called critical volume (VC).
What do you mean by permanent gases.?
Gases which has Z>1 that is show continuous positive deviation in Z(compressibility factor) value are permanent gases. These gases have lower value of critical temperature and can’t be liquefied easily.Examples:H2.He.N2 etc.
Give the examples of easily liquefiable gases.
CO2,NH3,H2O etc. are easily liquefiable gases which has having high critical temperature. These gases first show decrease in Z value with increasing pressure, which reaches a minimum value. On further increase in pressure, the value of Z increases continuously.
Which of these gases will liquefy first when we start cooling from 700 K to their critical temperature ? CO2,NH3,H2O, H2.He,N2,O2
H2O> NH3 >CO2> O2 >N2 >H2 >He. Higher the value of critical temperature easier is liquefaction.
Define vapour pressure.
In closed container when rate of evaporation is equal to the rate of condensation (equilibrium condition) the pressure exerted by the vapour of the liquid to the walls of the container is called vapour pressure.
What the boiling terms represent for liquid?
The condition of free vaporization throughout the liquid is called boiling.
Define boiling point?
The temperature at which vapour pressure of liquid is equal to the external pressure is called boiling point at that pressure.
What is normal boiling point.
The temperature at which vapour pressure of liquid is equal to the 1atm is called normal boiling point.
What is standard boiling point.
The temperature at which vapour pressure of liquid is equal to the 1 bar is called standard boiling point
Standard boiling point(99oC) of the liquid is slightly lower than the normal boiling point(100oC) why?
Since 1 bar pressure is slightly less than 1 atm pressure hence standard boiling point of the liquid is slightly lower than the normal boiling point.
The pressure cooker is used for cooking food on hills.
Since atmospheric pressure at high altitude is lower than sea level hence liquid boil at lower temperature on high altitude.Thus pressure cooker is used for cooking food on hills
Define Surface tension.
Surface tension is the force acting per unit length perpendicular to the line drawn on the surface of liquid.
What is the S.I unit of surface tension.
Nm-1
What is the cause of surface tension?
In the bulk of liquid, each molecule is pulled equally in every direction due to presence of similar molecules in all directions, resulting in a net force of zero.The molecules at the surface do not have other molecules on all sides, thus net attractive force is towards the interior of the liquid.
Liquid droplets are perfectly spherical in the gravity free environments why?
Surface tension is responsible for the shape of liquid droplets. It is the surface tension due to which liquids tend to have minimum surface area.
Why do liquid tends to rise (or fall) in the capillary.?
Surface tension gives stretching property to the surface of liquid hence liquid tends to rise (or fall) in the capillary.
Why do particles of soil at the bottom of river remain separated but they stick together when taken out?
It is due to surface tension which reduces surface area of thin film of water on particles of soil.
Heating makes sharp glass edges smooth why?
On heating, the glass melts and the surface of the liquid tends to take the rounded shape at the edges due to surface tension which makes the edges smooth.
Define viscosity.
Internal friction between layers of fluid which resist the flow if liquid is called viscosity.
Define laminar flow.
The flow of a viscous liquid on which particles of the fluid move in parallel layers and there is regular gradation of velocity in passing from one layer to the next layer is called laminar flow.
Obtain a formula for determining viscous force between two layers

Define coefficient of viscosity.
Viscosity coefficient is the viscous force when velocity gradient is unity and the area of contact is also unity.

Describe factors effecting viscosity.
(i)Temperature-higher the temperature lesser the viscosity ,this slower the motion.
(ii) Intermolecular force of attraction.- Hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces are responsible for viscosity.
Windowpanes of old buildings are thicker at the bottom than at the top why?
It is due to property of flow of liquid.
