Hydrogen
Hydrogen is placed separately in the periodic table why?
Hydrogen resembles both with alkali metals and halogens .At same time it also differs in many ways with those elements. Hydrogen is extremely small and H+doest not exist freely hence hydrogen is placed separately in the periodic table.
Properties to which hydrogen resembles with alkali metals.
1.Like alkali metals hydrogen can lose one electron to form unipositive ions.
2. Like alkali metals, hydrogen forms sulphide, oxides and halides.
3.Outermost electronic configuration of alkali metals(ns1) is similar to electronic configuration of hydrogen(1s1)
Properties to which hydrogen differs from alkali metals.
Ionisation enthalpy of hydrogen is very high unlike alkali metals which have low ionization enthalpies.
2. Hydrogen has not metallic properties.
Properties to which hydrogen resembles with halogens.
1.Like halogens hydrogen is also short by one electron to the corresponding noble gas configuration.
2. In term of ionization enthalpy, hydrogen is similar with halogens.
3. Like halogens, hydrogen forms a diatomic molecule.
How many isotopes of hydrogen are known.
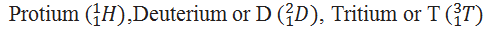
Which hydrogen is also known as heavy hydrogen.
Deuterium is also known as heavy hydrogen.
Are chemical properties of different isotopes are same? Explain in which property they differ from each other.
All isotopes of hydrogen have same electronic configuration hence they have almost the same chemical properties but their rates of reactions are different due to their different enthalpy of bond dissociation. Physical properties of these isotopes are different due their large mass differences.
What is water gas ?
The mixture of CO and H2 is called water gas.
What is syn gas?
Water gas (CO+ H2 ) is also known as synthesis gas (syn gas) because it is used for synthesis methanol and hydrocarbons.
What is ‘coal gasification’ ?
The process of producing ‘syn gas’ from coal is called ‘coal gasification’.
Hydrogen is inert at room temperature why or Atomic hydrogen is produced at a high temperature in an electric arc or under ultraviolet radiations.
The bond dissociation enthalpy of H-H is very high thus hydrogen gas is inert at room temperature.
Describe the different ways by which hydrogen combines with other element.
(i) Loss of an electron to give H +
(ii) Gain of an electron to form H–
(iii) Forms single covalent bond by sharing electrons.
Uses of Hydrogen?
(i) It is used as a rocket fuel.
(ii) In preparation of organic compound like methanol etc.
(iii) In preparation of inorganic compound like NH3 ,metal hydrides etc.
(iv) In hydrogenation of vegetable oils into vanaspati.
(v) In metallurgical processes, to reduce heavy metal oxides to metals.
(vi) In fuel cells to generate electrical energy.
Three types of hydrides.
(i) Ionic or saline or salt like hydrides.
(ii) Covalent or molecular hydrides.
(iii) Metallic or non-stoichiometric hydrides.
(i) Ionic or saline or saltlike hydrides.
These hydrides are formed with s block elements like Na ,K and Ca.
Exampes :NaH,KH,CaH2 etc.
Properties.
(i) Mainly ionic but some covalents hydrides are also available.
(ii) Crystalline, non-volatile and non conducting in solid state.
(ii) Covalent or molecular hydrides.
These hydrides are formed with P block elements like C,N.F etc
CH4, NH3, H2O and HF
Properties
(i) They are covalent hydrides.
(ii) Volatile compounds
(iii) Metallic or non-stoichiometric hydrides.
These are formed by many d-block and f-block elements. LaH2.87, YbH2.55, TiH1.5–1.
Properties.
(i) Nonstoichiometric, being deficient in hydrogen.
(ii) Crystalline, non-volatile and nonconducting in solid state.
Pd,Pt can use source of energy why?
These elements can accommodate large number of hydrogen thus they used as its
hydrogen storage and as a source of energy.
Different types of molecular hydrides
(i)Electron-deficient
(ii) Electron-precise
(iii) electron-rich
(i) Electron-deficient
Group 13 hydrides are electron-deficient compounds.like BH3.AlH3 etc.They all are electron acceptors that are Lewis acids.
(ii) Electron-precise
All elements of group 14 form such compounds example CH4 etc.
(iii) Electron-rich hydrides
Group 15-17 hydrides are electron-rich hydrides.Example: NH3 ,H2O, HF.They all are electron donors that are Lewis bases.
Water has high freezing point, high boiling point, high heat of vaporisation and high heat of fusion in comparison to H2S and H2Se why?
It is due to the presence of extensive hydrogen bonding between water molecules.
Which property of water is responsible for moderation of the climate and body temperature of living beings.
The high heat of vaporisation and heat capacity are responsible for moderation of the climate and body temperature of living beings.
What is the structure of ice?
Ice has crystalline structure in which each oxygen atom is surrounded tetrahedrally by four other oxygen.
Water acts as Bronsted acid and base both give reactions to prove it.
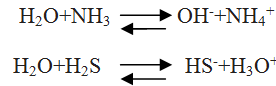
What is hard water and soft water?
Water which contains hydrogencarbonate, chloride and sulphate of calcium and magnesium called hard water. Water free from soluble salts of calcium and magnesium is called soft water.Hard water does not give lather with soap. Soft water gives lather with soap easily.
Hard water is unsuitable for laundry also why?
Hard water forms scum/precipitate with soap hence unsuitable for laundry.
Hard water is harmful for boilers why?
On boiling there is deposition of salts in the form of scale. This reduces the efficiency of the boiler.
Types of hardness of water?
Hardness of water is of two types:
(i) Temporary hardness
Temporary hardness is due to the presence of magnesium and calcium hydrogen carbonates
(ii) Permanent hardness
Permanent hardness is due to the presence of magnesium and calcium chlorides and sulphates.
Methods to remove temporary hardness.
(i)Boiling
Mg(HCO3)2 ⎯⎯⎯⎯→Mg(OH)2 ↓ + 2CO2 ↑
Ca(HCO3)2 ⎯⎯⎯⎯→CaCO3 ↓ +H2O+ CO2 ↑
Mg (OH)2 and CaCO3 are insoluble in water.
(ii)Clark’s Method
Mg(HCO3)2+ 2Ca(OH)2 ⎯⎯⎯⎯→ 2CaCO3↓ + Mg(OH)2 ↓ + 2H2O
Ca(HCO3)2+ Ca(OH)2 ⎯⎯⎯⎯→ 2CaCO3↓ + 2H2O
Mg (OH)2 and CaCO3 are insoluble in water.
Methods to remove permanent hardness.
(i)Treatment with washing soda
MCl2+Na2CO3⎯⎯⎯⎯→MCO3↓+2NaCl
MSO4 +Na2CO3⎯⎯⎯⎯→MCO3↓+Na2SO4
M=Mg and Ca
(ii) Calgon’s method
Na6P6O18 ⎯⎯⎯⎯→ 2Na++ Na4P6O182-
(M =Mg, Ca)
M2++ Na4P6O182- ⎯⎯⎯⎯→2Na++ [M2P6O18]2-
M=Mg and Ca
What do you mean by 100 volume hydrogen peroxide?
30% solution of H2O2 is known as 100 volume hydrogen peroxide. It means 1 ml of 30 % H2O2 gives 100ml of oxygen at STP.
What are the uses of H2O2?
(i) Used as a hair bleach and as a mild disinfectant.
(ii) Perhydrol is H2O2 used as antiseptic
(ii) In manufacturing sodium perborate and per-carbonate, which are used in high quality detergents.
(iii) In the synthesis of hydroquinone, tartaric acid, pharmaceuticals (cephalosporin) etc.
(iv)Used as a bleaching agent for textiles, paper pulp, leather, oils etc.
What is heavy water?
D2O, used as a moderator in nuclear reactors.
What are the advantage of using hydrogen as fuel?
(i)On a mass for mass basis dihydrogen can release more energy than other sources of fuel
(ii) Pollutants in combustion of dihydrogen are less than other sources of fuel.
What are the disadvantages of using hydrogen as fuel cell?
1. Mass of a cylinder containing compressed dihydrogen of will be very high.
2.Expensive insulated tanks will be used to convert hydrogen gas into liquid.
What will be only possible pollutants of fuel cell?
The only pollutants will be the oxides of dinitrogen.
What is the basic principle of hydrogen economy?
To transport and store of energy in the form of liquid or gaseous dihydrogen. Advantage of hydrogen economy is that energy is transmitted in the form of dihydrogen and not as electric power.
