Thermodynamics
Define system and surrounding.
Substance which is taken under observation is called system , rest of the universe is called surrounding.
Explain the different types of system with example.
There are three types of system.
(i)Open system.
The type of system in which both matter and energy is exchanged between system and surroundings.
Example: Substance in open container.
(ii) Closed system.
Example: Substance in close container having thermoconducting wall.
The type of system in which only energy is exchanged between system and surroundings.
(iii) Isolated system.
The type of system in which neither matter nor energy is exchanged between system and surroundings.
Example: Substance in insulated vessel (Thermos flask)
Define state function or state variables and path function.
Those properties of the system which depend only on the state of the system and not on how it is reached to that state are called state function.
Examples:Pressure,Temperature,Volume ,Internal energy,Enthalpy.etc.
Those properties of the system which depend on how the change is carried out are called path function.
Examples:Heat energy(q),Work done(w)
Define internal energy (U).
The total energy contained by the system is called internal energy.
U=Kinetic energy + Potential energy
Kinetic energy=translational energy + rotational +vibrational.
What is adiabatic system?
The types of the system in which there is no heat exchange between the system and surroundings through its boundary is called adiabatic system.
What is the difference between adiabatic system and isolated system.
Adiabatic system is a specified condition
Mention the sign convention for different thermodynamics function.
Energy absorbed by the system ‘q’=+ve
Energy released by the system ‘q’ =-ve
Work done by the system ‘w’ = -ve
Work done on the system ‘w’ = +Ve
Define first Law of thermodynamics.
Internal energy change of the system is equal to the energy provide to the system and work done by the system.
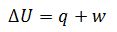
Obtain a formula for mechanical work (pressure- volume work) against constant external pressure .

What do you mean by free expansion?
Expansion of a gas in vacuum when is called free expansion.
No work during free expansion of an ideal gas whether the process is reversible or irreversible.
Define reversible and irreversible process.
The process which occur infinitely slowly such that system and surrounding are always in equilibrium with each other. The process can be reversed at any moment by an infinitesimal change called reversible process. An irreversible process can be defined as a process in which the system and the surroundings do not return to their original condition once the process is initiated
Change in internal energy of a system when
(i)Work done by the system or on the system and heat is absorbed by the system.
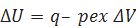
(ii)If a process is carried out at constant volume and heat is absorbed by the system.

(iii) For isothermal process.
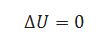
(iv) For adiabatic system.

What is the equation for calculating work done for isothermal irreversible process.
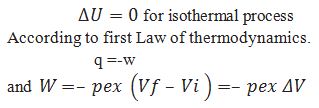
Obtain equation for the work done for the isothermal reversible process.

Define enthalpy.
A thermodynamic function, the enthalpy H is equal to H = U + pV .
U=Internal energy of the system
P=Pressure of the system.
V=Volume of the system.
What will be the change in enthalpy during the reaction at constant pressure.
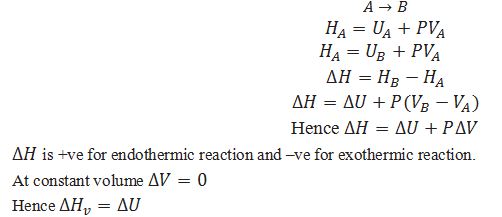
What is the equation for calculating change in enthalpy at constant pressure for a reaction involving gases.

What is extensive property and intensive properties of a system?
Those properties which depends on the amount of matter present in the system are called extensive property.Example: Mass, volume, internal energy, enthalpy.
Those properties which do not depend on the amount of matter present in the system are known as intensive properties.Example:Temperature, density, pressure etc.
Define heat capacity.
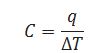
Heat requires by the substance to increase the temperature by one 0C is called heat capacity.
Define specific heat capacity.

Heat requires by the unit mass of the substance to increase the temperature by one 0C is called specific heat capacity.
What is the relation between heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) and heat capacity at constant pressure Cp)?
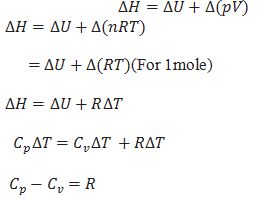
What is bomb calorimeter?
A calorimeter in which the chemical reaction is carried out at constant volume. Hence there is no work done.
How can we calculate the enthalpy change for reaction?
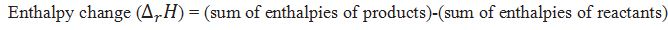
Define standard enthalpy of reaction.
The standard enthalpy of reaction is the enthalpy change that occurs on a system when one mole of matter is transformed by a chemical reaction under standard condition.
Define standard enthalpy of fusion

Enthalpy of fusion is the change in enthalpy when one mole of solid is melted in liquid.
Define standard enthalpy vaporization

Amount of heat required to vaporize one mole of liquid at constant temperature.
Define standard enthalpy of sublimation
The change in enthalpy when one mole of a solid substance is converted into vapour state at constant temperature.
Define standard enthalpy of formation
Enthalpy change during the formation of one mole of a compound from its constituent element in their standard state.

Define enthalpy of combustion
Enthalpy change during combustion of one mole of a substance when all the reactants and products are in standard state.
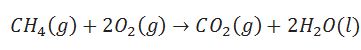
Define enthalpy of atomisation.
(i )Enthalpy change during breaking of one mole of bond of a compound completely into gaseous state.
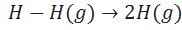
(ii)Enthalpy of atomization is also called enthalpy of sublimation in case of solid element.

Define bond dissociation enthalpy.
The bond dissociation enthalpy is the change in enthalpy when one mole of covalent bond is broken to form product in gaseous state.
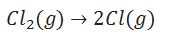
Define mean bond enthalpy.
For the polyatomic molecules mean bond enthalpy is defined as total bond dissociation enthalpies divided by number of bonds.
Define Hess’s Law of constant heat summation.
When a reaction takes place in several steps then its standard enthalpy is the sum of the standard enthalpies of the intermediate reactions.
Define enthalpy of solution
Enthalpy change when one mole of substance is dissolved in given amount of solvent.
Define lattice enthalpy.
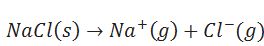
The enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic compound dissociates into it constituent ions in gaseous state.
Define enthalpy of hydration.
The energy released when new interacting are made between the gaseous ions and water molecules is called hydration enthalpy.
What is the relationship between enthalpy of solution,lattice enthalpy,hydration enthalpy.
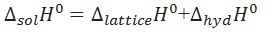
What is Born -Haber cycle.
With the help of Born-Haber Cycle we determine the lattice enthalpy of the substance.

Define spontaneous reaction.
The reaction which occurs itself without any external force is called spontaneous reaction.
Examples:Burning of carbon in oxygen.Cooling of hot water.
What do you mean by spontaneity of chemical reaction?
Spontaneity means feasibility of particular chemical reaction that is that reaction is possible or not.
What is the criteria for spontaneous process?

Define entropy(s)
The degree of randomness or disorderness is called entropy.
How can we calculate the change in entropy of a reversible reaction?
Where q=enthalpy change during chemical reaction or heat released or absorbed by the system.
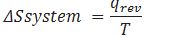
What is the relation between change in entropy of the system ,change in entropy of surrounding )?
What is the relation between change in entropy of the system. change in enthalpy of system ) and Gibbs energy change ?
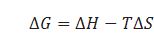
In that case in which randomness increases the change in entropy is taken as +ve and when randomness decreases the change in entropy is taken as –ve.
What is the formula for calculating equilibrium constant Kc?
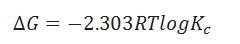
When the particular reaction is non spontaneous, spontaneous and equilibrium according to .
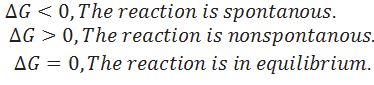
Predict whether the reaction may occur spontaneously or not in following cases.

