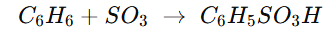Oleum, also known as fuming sulfuric acid, is a highly reactive compound consisting of dissolved sulfur trioxide gas (SO₃) in 100% sulfuric acid.
What do you mean by fuming?
When we say “fuming” (like fuming sulfuric acid = oleum), we mean:
- The liquid gives off visible vapors (“fumes”) when exposed to air.
- In the case of oleum, those vapors are actually SO₃ gas, which escapes easily because SO₃ is volatile.
- When this SO₃ gas meets moisture in the air, it reacts immediately to form tiny droplets of H₂SO₄, which look like white, smoky fumes.

That’s why:
- Concentrated H₂SO₄ does not “fume” much in air.
- Oleum does, because of the escaping SO₃.
So fuming = releasing visible vapors (SO₃ + H₂SO₄ mist) into the air
Fumes of H2SO4 dangerous?
Yes ✅ the fumes of H₂SO₄ (sulfuric acid) are very dangerous.
Here’s why:
- What the fumes are:
Pure H₂SO₄ itself doesn’t evaporate much, but when it’s very concentrated (or as oleum) it releases SO₃ vapors.
These vapors react with moisture in the air → form fine droplets of H₂SO₄ mist. - Effects on health:
- Extremely corrosive to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
- Causes severe burns on contact.
- If inhaled, can damage the nose, throat, lungs (leading to breathing difficulty, pulmonary edema).
- Even short exposure to strong fumes is harmful.
That’s why handling concentrated H₂SO₄ / oleum requires fume hoods, protective gloves, goggles, and masks.
H₂S₂O₇ is the chemical formula of oleum?
Oleum is also called fuming sulfuric acid.
It is not a single pure compound but rather a solution of SO₃ dissolved in H₂SO₄.
H₂S₂O₇ = pyrosulfuric acid, which represents one particular composition of oleum (when there is exactly one mole of SO₃ combined with one mole of H₂SO₄).
Oleum in general can have different amounts of SO₃, not just the 1:1 case.
If it is mixture, so why it is represented by molecular formula H2S2O7?
Oleum is really a mixture (H₂SO₄ + SO₃), but in chemistry we often like to represent it in a molecular way. That’s why one of its possible compositions is written as H₂S₂O₇ (pyrosulfuric acid).
Convenience in Representation
- Writing H₂S₂O₇ makes it easier to handle in equations and discussions, instead of always writing “H₂SO₄·SO₃”.
- For example, when balancing reactions in textbooks, H₂S₂O₇ is simpler to use.
But in Reality

- Oleum is not just H₂S₂O₇ — it may have more (or less) SO₃ dissolved in H₂SO₄.
- So H₂S₂O₇ is only one specific case of oleum.
Why Sulphonation of OF BENZENE IS Carried out with Oleum not pure Conc. H2SO4?
leum already contains a large amount of free SO₃ dissolved in H₂SO₄.
That SO₃ directly acts as the electrophile in the sulphonation of benzene.
The H₂SO₄ in oleum helps by protonating SO₃ to form the stronger electrophile