A carbene is a highly reactive organic species in which a carbon atom has only six valence electrons (instead of the usual eight) and is bonded to two substituents.
General Features:
- General formula: R₂C:
- Structure: Carbon in carbene is divalent (forms 2 bonds).
- Electron deficiency: Only 6 valence electrons → makes carbenes very reactive.
- Bond angle: Usually about 104–150°, depending on type.
Types of Carbenes:
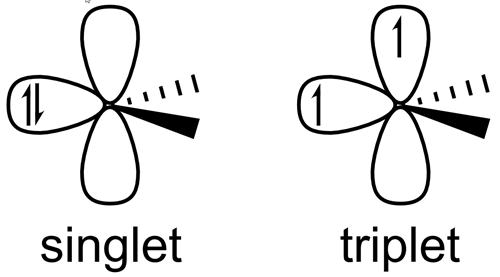
- Singlet carbene
- Both non-bonded electrons are paired in the same orbital.
- Usually bent structure (~104° bond angle).
- Electrophilic (electron-loving).
- Triplet carbene
- The two non-bonded electrons occupy different orbitals with parallel spins.
- Linear or nearly linear structure (~130–150° bond angle).
- More stable than singlet.
Examples:
- Methylene (:CH₂) → simplest carbene.
- Dichlorocarbene (:CCl₂) → formed in Reimer–Tiemann reaction.
Preparation:
- By photolysis or pyrolysis of diazo compounds (e.g., CH₂N₂ → :CH₂ + N₂).
- By decomposition of haloforms (CHCl₃ + base → :CCl₂).
Reactivity:
- Carbenes add to double bonds → form cyclopropanes.
- Insert into C–H bonds.
- Highly reactive intermediates in organic chemistr