The s-block elements
Why are group 1 and group 2 elements called s-block elements?
The last electron of these elements enters the outermost s-orbital that is why they are called s-block elements.
Group1 elements are collectively known as alkali metals why?
They form hydroxide in water,which are alkaline in nature ,that is why they are called alkali metals.
Group 2 elements are collectively known as alkaline earth metals why?
Because their oxides and hydroxides are alkaline in nature and these metal oxides are found in the earth’s crust.
What is general electronic configuration of s-block elements?
ns1-2
GROUP 1 ELEMENTS ( ALKALI METALS)
Li, Na, K,Rb,Cs,Fr
Q.1.Alkali metals are normally kept in kerosene oil why?
Ans.Alkali metals are highly reactive towards air and water hence they are normally kept in kerosene oil.
Q.2.Alkali metals are never found free in nature why?
Ans. Due to very large size and presence of only one electron in outermost shell they easily lose their valence electron and from M+ ion.
Q.3.The atomic and ionic radii of alkali metals increase on moving down why?
Ans. As moving down the group number of shell increases, that is why atomic and ionic radii of alkali metals increase top to bottom.
Li<Na<K<Rb<Cs
Q.4.The ionization enthalpies of the alkali metals are considerably low and decrease down the group from Li to Cs.
Ans.Alkali metals are very large hence ionization enthalpies of these metals are very low. Since atomic size increases down the group thus ionization enthalpy decreases down the group.
Q.5.The hydration enthalpies of alkali metal ions decrease with increase in ionic sizes why?
Ans.Atomic size increases down the group hence hydration enthalpy decreases down the group.
Li+> Na+ > K+ > Rb+ > Cs+
Q.5. Li+ has maximum degree of hydration why?
Or
Why are lithium salts commonly hydrated and those of the other alkali ions usually anhydrous?
Ans. Li+ is smallest in size thus lithium salts are mostly hydrated example LiCl.2H2O
Q.6.Alkali metals have very low density why?
Ans. Alkali metals are very large hence they have very low density.
Q.7.Why does density of alkali metals increases down the group Why ?
Ans. Because mass increases down the group.
Q.8.Potassium is lighter than sodium why ?
Ans. In case of K electron filling takes place in 4s without 3d thus volume increases so much and density decrease.
Q.9.The melting and boiling points of the alkali metals are low why?
Ans.Weak metallic bonding in alkali metal crystal due to the presence of only a single valence electron in them.
Q.10.Alkali metals give flame test why?
Ans.Outermost orbital electron is excited to higher energy level .When the excited electron comes back to the ground state, there is emission of radiation in the visible region. Therefore they can be detected by the respective flame tests.
Q.11. Cs and K are used in photoelectric cell why?
Ans.The light energy absorbed by these metals and lose electron because outermost electron is loosely bonded with nucleus.
Q.12.Alkali metals are very reactive why?
Ans. Due to very large size and low ionization enthalpy alkali metals are highly reactive.
Q.13.Alkali metals tarnish in air why?
Ans. Alkali metals form oxide with air which further reacts with water and form hydroxide.
Q.14.What is the nature of oxide of alkali metals.
Ans. Lithium forms monoxide, sodium forms peroxide and K, Rb and Cs forms superoxide
4 Li +O →2Li2O (oxide)
2Na +O2 →Na2O2 (peroxide)
M+O2 →MO2 (superoxide)
(M = K, Rb, Cs)
Q.15.Lithium reacts directly with nitrogen of air to form the nitride, Li3N why?
Ans.It is due to very small size of Li it shows anomalous behavior.
Q.16.What is the oxidation state of K in KO2?
Ans +1
Q.17.Li is least reactive with water but other elements react explosively with water why?
Ans. It is due to small size and very hydration energy of lithium it is least reactive with water.
Q.18.All the alkali metal hydrides have high melting points why?
Ans. Alkali metals are ionic solid that is why they have high melting point.
Q.19.Lithium salts are mainly covalent why?
Ans. Li+ is small in size hence distortion of electron cloud(polarization power) is maximum hence its salt is covalent.
Q.20.In all lithium salts LiI is most covalent and why?
Ans. I– having large size thus polarization power is maximum.
Q.21.Lithium is strongest reducing agent why?
Ans. EO value depends on the following factors.
M (s) → M(g) (Sublimation enthalpy)
M(g) → M(g)+ (Ionization enthalpy)
M+(g) + H2O → M+(aq) Hydration enthalpy
Due to small size of lithium ,it has the highest hydration enthalpy resulting low negative Eo value and its high reducing power.
Q.22.Alkali metals give blue color in liquid ammonia.
or
Alkali metals are paramagnetic in liquid ammonia why?
Ans. M +(x + y) NH3 →[M(NH3 )x ]+ + [e(NH3 )y ]−
Due to presence of ammoniated electron alkali metals give blue color in liquid ammonia solution.
Q.23 Alkali metals in liquid ammonia liberate hydrogen on standing give reaction.
Ans. M+ (am) + e− + NH3 (1)→MNH2(am) +½H2(g)
Q.24.What are the different uses of lithium alloys?
Ans. Li+Pb= ‘White metal’ bearings for motor engines,
Li+Al = Aircraft parts
Li+Mg= Armour plates which is used in thermonuclear reactions.
Q.25.What are the uses of other alkali metal.
Ans 1.Liquid sodium metal is used as a coolant in fast breeder nuclear reactors.
2. Na/Pb alloy needed to make PbEt4 and PbMe4 which is used as anti knock additives to petrol earlier.
3. Potassium hydroxide is used in manufacturing of soft soap.
4. Potassium chloride is used as a fertilizer.
5. Cesium is used in photoelectric cells.
Q.26.What is the reason behind the increasing stability of the peroxide or superoxide, as the size of the metal ion increases ?
Ans.It is due to the stabilisation of large anions by larger cations through lattice energy effects.
Q.27. Why is KO2 paramagnetic?
Ans. An unpaired electron is present antibonding π*2p orbital of O2-
Q.28.The alkali metal halides, MX, (X=F,Cl,Br,I) are all high melting crystalline solids Why?
Ans. Alkali metals halides are ionic compound hence have very high melting point.
Q.29.The melting and boiling points of alkali metals decreases in following order fluoride > chloride > bromide> iodide why?
Ans.Metallic bond strength decreases as the size of halide ion increases.
Q.30. All alkali metal halides are soluble in water why.
Ans. Due to weak metallic bonding in alkali metal lattice enthalpy is lower than hydration enthalpy.
Q.31.Solubility of LiF in water is low why?
Ans.High lattice enthalpy of LiF due to small size of F.
Q.32.Solubility of CsI in water is low why?
Ans.Low hydration enthalpy of CsI due to large size of Cs.
Q.33.LiCl, LiBr,and LiI are not only soluble in water but also soluble in organic solvent like acetone,ethanol etc,but LiF is almost insoluble in water.
Ans Difference in lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy of other litium halides is higher than LiF, hence lithium halides are soluble in water. Due to larger size of Cl,Br and I their lithium halides have higher covalent character ,hence they are soluble in organic solvent also.
Q.34.The mobilities of the alkali metal ions in aqueous solution are Li+ < Na+ < K+ < Rb+ < Cs+
Ans.As the size of alkali metal ions increases hydration extent of these ions decreases thus mass of hydration ion decreases thus mobility increases.
Q.35.LiI is more soluble in KI in ethanol why?
Ans.LiI is more covalent than than KI due to high polarization power of Li in compare with K.Thus LiI is more soluble in KI in ethanol.
Q.36.Sodium is found to be more useful than potassium why?
Or
What are the biological function of Na and K.
Ans.Na+ ions are found in the blood plasma and also in interstitial fluid which surrounds the cell thus help in variety of biological function.
1.Transmission of nerve signal.
2.Regulate the flow of water across cell membrane.
3.Transport sugar and amino acids into cell.
K+ ions are found inside cell and help in following biological functions.
1.They activate many enzymes
2.Participate in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP.
From above observation we can say that Sodium is found to be more useful than potassium.
Q.37.Alkali metals are prepared by electrolysis of their fused chlorides why?
Ans.In aq alkali metals chlorides H+ ions are present along with alkali metals ions,and Eo value of H+ is higher than alkali metal ions hence H2 instead of the alkali metals produced at cathode.
Q.38.A solution of Na2CO3 is alkaline why ?
Ans. In aq solution forms NaOH which is strong base.
CO32- + H2O → HCO3– +OH–
Q.39.Define oxoacids.
Ans.Oxo-acids are those in which the acidic proton is on a hydroxyl group with an oxo group attached to the same atom e.g., carbonic acid.
Q.40.The stability of the carbonates and hydorgencarbonates of alkali metal increases from top to bottom in group why?
Ans.As the size of alkali metal ions increases the polarization power of these ions to CO32- and HCO3– decreases hence thermal stability increases.
Q.41.Lithium carbonate is not so stable to heat why?
Or
Why is Li2CO3 decomposed at a lower temperature whereas Na2CO3 at higher
temperature?
Ans. smaller Li+ ions polarize CO32 most hence it decomposes into Li2O and CO2.
Q.42. Why does Li show anomalous behavior?
Ans It is due to
(i) Exceptionally small size of its atom
(ii) High polarising power
(iii)High charge/radius ratio.
Q.43.List some anomalous behavior of Li.
Ans. (i) m.p. and b.p.of Li are higher than the other alkali metals.
(ii) Lithium is least reactive but the strongest reducing agent among all the alkali metals.
(iii) Li forms monoxide, Li2O
(iv)Li forms nitride Li3N unlike other alkali metals.
(v) LiCl is more hydrated in compare with other alkali metals.
(vi) Solid Lithium hydrogencarbonate doesn’t exist while all other elements form solid hydrogencarbonates.
(vii) Lithium unlike other alkali metals forms covalent compound.
Q.44.What is the reason of diagonal relationship between Li and Mg.
Ans Due to similar charge/radius ratio they show similar behavior.
Q.45.What are the points of similarities between Li and Mg.
Ans (i)Both lithium and magnesium are harder than other elements in the respective groups.
(ii) Both Lithium and magnesium react slowly with water.
(iii) Both form nitride Li3N and Mg3N2, by direct combination with nitrogen.
(iv) Both form monoxide with oxygen Li2O and MgO.
(v) The carbonates of lithium and magnesium decompose easily on heating to form the oxides and CO2.
(vi) Solid hydrogencarbonates are not formed by lithium and magnesium.
(vii) Both LiCl and MgCl2 are soluble in ethanol.
(viii) Both LiCl and MgCl2 are deliquescent and crystallise from aqueous solution as hydrates, LiCl·2H2O and MgCl2·8H2O.
Q.46.Potassium carbonate cannot be manufactured by Solvay process why?
Ans.Potassium hydrogencarbonate is too soluble to be precipitated by the addition of ammonium hydrogencarbonate to a saturated solution of potassium chloride.
Q.47.What is the heating effect of washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O)?

Q.48.What are the different uses of washing soda .
Ans.1 Water Softening,Laundring process.
2 In paper ,Textiles and Paint industries.
3 To manufacture soap,glass and borax.
Q.49. What are the uses of NaCl?
Ans.1Common salt for domestic purpose.
2 To prepare Na2O2.MaOH etc.
Q.50.What are the uses of NaOH (Caustic Soda)?
Ans. (i) To manufacture soap paper, artificial silk etc
(ii) In petroleum refining
(iii) In the purification of bauxite,
(iv) As a laboratory reagent.
Q.50.What are the uses of Sodium hydrogencarbonate (baking soda)
Ans (i) As antiseptic.
(ii) It is used in fire extinguishers.
Q.51.What are the common physical and chemical properties of alkali metals?
Ans.Physical properties.
(i) Crystalline solid
(ii) Silvery white, soft and light metals.
(iii) Low density
(iv) Low melting and boiling point
(v) Give flame test
Chemical properties
(i) Very highly reactive
(ii)+1 is common oxidation state
(iii) Form monoxide ,peroxide ,super oxide with oxygen
(iv) Form strong base on water
(v) Form halides with halogen
(vi) All are very strong reducing agent.
(vii) Their ammonical solution is deep blue and paramagnetic
Q.52.What is the oxidation state of Na in Na2O2.
Ans . (+1) In peroxide oxidation state of oxygen is -1 hence
2(x) -2=0 thus x=1
Q.53.Sodium is less reactive than potassium why?
Ans.Lower ionization enthalpy of K makes it more reactive than sodium.
Q.54.Alkali and alkaline earth metals can not be obtained by chemical
reduction methods why?
Ans. Alkali and alkaline earth metals are themselves strong reducing agent due to low ionization enthalpies thus reducing agents better than alkali metals are not available.
Q.55.Why are K and Cs rather than Li used in photoelectric cell?
Ans.Atomic size of K and Cs is much larger than Li thus light can easily emits electron from K and Cs.
Q.56.Arrange thermal stability of carbonate and hydrogencarbonate of alkali metals in increasing order.
Ans.Li2CO3 <Na2CO3< K2CO3< Rb2CO3< Cs2CO3
LiHCO3 <NaHCO3< KHCO3< RbHCO3< CsHCO3
GROUP 2 ELEMENTS ( ALKALINE EARTH METALS)
Be,Mg,Ca,Sr,Ba,Ra
Q.1.The atomic and ionic radii of alkaline earth metals increase on moving down why?
Ans As moving down the group number of shell increases, that is why atomic and ionic radii of alkaline earth metals increases top to bottom.
Be<Mg<Ca<Sr<Ba
Q.2.The first ionization enthalpy of the alkali metals is lower than corresponding alkaline earth metal why?
Ans.Alkali metals are larger than alkaline earth metals hence ionization enthalpies of these metals are lower than corresponding alkaline earth metals.
Q.3.The 2nd ionization enthalpy of the alkaline earth metals are lower than corresponding alkali metal why?
Ans.After removing of one electron from alkali metals they are converted into stable inert gas configuration hence removing of second electron becomes difficult.
Q.4.The hydration enthalpies of alkaline metal ions decrease with increase in ionic sizes why?
Ans.Atomic size increases down the group hence hydration enthalpy decreases down the group.
Be2+> Mg2+ > Ca2+ > Sr2+ > Ba2+
Q.5.Hydration enthalpies of alkaline earth metal ions are larger than those of alkali metal ions.?
Ans. Ionic size of alkaline earth metals are lower than alkali metal ions hence the hydration enthalpies of alkaline earth metal ions are larger than those of alkali metal ions.
Q.6.The alkaline earth metals are harder than the alkali metals why?
or
The melting and boiling points of these metals are higher than the corresponding alkali metals
Ans. Inter atom metallic bonding is stronger in case of alkaline earth metals due to their lower size.
Q.7.Strontium and barium impart characteristic colours to the flame why?
Ans. Flame excites electrons to higher energy levels and when they come back to the ground state, energy is emitted in the form of visible light.
Q.8.Beryllium and magnesium do not give flame test why?
Ans Electrons in beryllium and magnesium are too strongly bound to get excited by flame. Hence, these elements do not impart any colour to the flame.
Q.9.The alkaline earth metals are less reactive than the alkali metals?
Ans.Ionisation enthalpy of alkaline earth metals is higher than alkali metal hence alkaline earth metals are less reactive than the alkali metals.
Q.10.Beryllium and magnesium are kinetically inert to oxygen and water why?
Ans.Be and Mg form of an oxide film on their surface hence further reaction is not possible.
Q.11.Alkaline earth metals are strong reducing agents why?
Ans.It is due to large negative values of their reduction potentials.
Q.12.Reducing power of alkaline earth metal is less than those of their corresponding alkali metals why?
Ans.Alkali metals have larger –ve reduction potential due to their lower ionization enthalpies.
Q.13.The alkaline earth metals dissolve in liquid ammonia to give deep blue black solutions why?
Ans. Alkaline earth metals dissolve in liquid ammonia to give deep blue black solutions due to formation of ammoniated ions.
M +(x + y)NH3 → [M(NH3 )x ]2+ + 2[e(NH3 )y ]−
Q.14.What are the uses of different alkaline earth metals?
Ans.1.Cu +Be alloy is used in prepare high strength springs
2. Metallic beryllium is used for making windows of X-ray tubes.
3. Mg-Al alloys are used in air-craft construction
4. Magnesium (powder and ribbon) is used in flash powders and bulbs, incendiary bombs and signals
5. A suspension of magnesium hydroxide in water (called milk of magnesia) is used as antacid in medicine.
6. Magnesium carbonate is an ingredient of toothpaste.
7. Calcium is used in the extraction of metals from oxides which are difficult to reduce with carbon.
8. Radium salts are used in radiotherapy, for example, in the treatment of cancer.
Q.15.Alkaline earth metals compounds are less ionic than the corresponding compounds of alkali metals.
Ans .It is due to increased nuclear charge and smaller size of alkaline earth metals they distort electron cloud higher than the alkali metals.
Q.16.The fluorides of alkaline earth metals are relatively less soluble than the chlorides why?
Ans.The fluorides of alkaline earth metals have higher lattice energy than the chlorides.
Q.17.The solubility of alkaline earth metal hydroxides in water increase down the group why?
Ans.Both lattice enthalpy and hydration enthalpy decreases down the group. OH– is common hence size of the cation decides the lattice enthalpy. Since lattice enthalpy decreases much more than the hydration enthalpy with increasing ionic size, the solubility increases as we go down the group.
Q.18.Solubility of alkaline earth metal carbonates and sulphates in water decreases down the group Why?
Ans.The size of anions(CO32-and SO42-) are much larger compared to cations, the lattice enthalpy will remain almost constant within a particular group. Since the hydration enthalpies decrease down the group, solubility will decrease as found for alkaline earth metal carbonates and sulphates.
Q.19.Arrange the thermal stability of carbonates and sulphates in decreasing order.
Ans.As the size of ion increase, ability to polarize the negative part decreases hence thermal stability increases.
Thus BeCO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 < SrCO3< BaCO3
BeSO4 < MgSO4 < CaSO4 < SrSO4< BaSO4
Q.20.Beryllium carbonate is unstable and can be kept only in the atmosphere of CO2 why?
Ans. Being very small size it polarize CO32- most hence it is unstable and can be kept only in the atmosphere of CO2
Q.21.Arrange the thermal stability of alkaline earth metal hydroxide in decreasing order.
Ans.Be(OH)2 < Mg(OH)2 <Ca(OH)2< Sr(OH)2 <Ba(OH)2
Q.22.Arrange the basic strength of alkaline earth metal hydroxide in decreasing order.
Ans. Be(OH)2 < Mg(OH)2 <Ca(OH)2< Sr(OH)2 <Ba(OH)2
Q.23.Why are alkaline earth metal hydroxide are less basic, less stable and less soluble than alkali metal hydroxides?
Ans. Lower size, higher ionization enthalpy and higher lattice enthalpy of alkaline earth metals hydroxide are responsible for their less basic and less stable than alkali metal hydroxides?
Q.24.One of the alkaline earth metal hydroxide are amphoteric in nature name that hydroxide.
Ans.Be(OH)2 is amphoteric in nature because it reacts both with alkali and acid.
Q.25.Except Beryllium halides all other halides of alkaline earth metals are ionic in nature why?
Ans.Be is small atom hence it distorts electron cloud towards it most hence it forms mainly covalent halides.
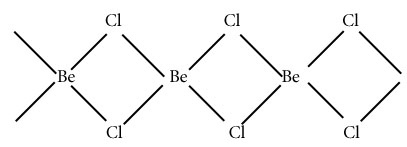
Q.26.Draw the structure of beryllium chlorides in solid state and in vapour state.
Ans. In solid state it exists in polymeric form with monomer BeCl2,and in vapour state it forms chloro-bridged dimer.

Q.27.The tendency to form halide hydrates gradually decreases (for example, MgCl2·8H2O, CaCl2·6H2O, SrCl2·6H2O and BaCl2·2H2O) down the group.
Ans.Since size of the alkaline earth metal decreases top to bottom hence hydration strength decreases down the group.
Q.28. List some anomalous behavior of Be.
Ans 1.Compunds of Be are mainly covalent.
2.Be can show maximum coordination number 4 but other elements can show coordination number more than 4.
3. The oxide and hydroxide of beryllium, the group, are amphoteric in nature.
Q.29.List some similar behavior of Be and Al.
Ans. Due to similar charge/radius ratio beryllium resembles aluminum in some ways.
(i) Both Be and Al are not readily attacked by acids.
(ii)Both Beryllium and aluminium hydroxide dissolve in excess of alkali to give a beryllate ion, [Be(OH)4]2– just as aluminum hydroxide gives aluminates ion, [Al(OH)4]–.
(iii) in vapour state the chlorides of both beryllium and aluminum exist in bridged chloride structure
(iv)Both the chlorides are soluble in organic solvents and are strong Lewis acids.
Q.30.Define the process slaking of lime.
Ans.The addition of limited amount of water breaks the lump of lime. This process is known as slaking of lime.
Q.31.What are the uses of quick lime(CaO).
Ans.(i)Used in manufacturing cement.
(ii) Used in manufacturing sodium carbonate from caustic soda.
(iii) In the purification of sugar
(iv)In the manufacture of dye stuffs.
Q.32.What do you mean by lime water and milk of lime?
Ans.The aqueous solution of Ca(OH)2 is called lime water and a suspension of slaked lime in water is called milk of lime.
Q.33.When CO2 is passed through lime water turns milky why?
Ans Due to formation of calcium carbonate.
Q.34.What are the uses of Calcium hydroxide(slaked lime)?
Ans. (i) Used in the preparation of mortar.
(ii)Used in white wash due to its disinfectant nature.
(iii)Used in making glass and preparation of bleaching.
Q.35.What are the uses of CaCO3 ?
Ans.(i) As an antacid
(ii) Mi ld abrasive in tooth paste.
(iii) A constituent of chewing gum.
(iv) Filler in cosmetics.
(V) Used in the manufacture of high quality paper.
Q.36.What do you mean by ‘dead burnt plaster’.
Ans. It is anhydrous calcium sulphate having no water of crystallisation formed after heating plaster (CaSO4 .1/2H2O ) of Paris above 393K.
Q.37.What are the uses of plaster of Paris(CaSO4 .1/2H2O)?
Ans. (i)In the building industry.
(ii) As plasters.
(iii) In ornamental work.
(iv)For making casts of statues and busts.
Q.38.Cement is is also called Portland why?
Ans. It resembles with the natural limestone in the Isle of Portland, England.
Q.39.What are the composition of cement.
Ans. The averagecomposition of Portland cement is : CaO, 50-60%; SiO2, 20-25%; Al2O3, 5-10%; MgO, 2-3%; Fe2O3, 1-2% and SO3, 1-2%.
Q.40.What do you mean by setting of cement?
Ans.When water is mixed with cement it gives give a hard mass, due to the hydration of the molecules of the constituents and their rearrangement.
Q.41.Why gypsum is added to cement?
Ans.Gypsum slow down the process of setting of the cement so that it gets sufficiently hardened.
Q.42.What are the biological use s of alkaline earth metals.
Ans (i)Chlorophyll contains magnesium.
(ii)Ca is present in bones and teeth.
(iii) Ca plays important roles in neuromuscular function,interneuronal transmission, cell membrane integrity and blood coagulation.
