Equilibrium
Equilibrium in different physical process.
Solid-liquid equilibrium.
Rate of transfer of molecules from solid into liquid and of reverse transfer from liquid into solid is equal at normal melting point or normal freezing point of the substance.

Liquid -vapour equilibrium.
When rate of evaporation is equal to rate of condensation at normal boiling point of
the liquid.
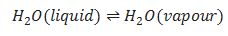
Solid-vapour equilibrium.
Rate of transfer of molecules from solid into vapour and of reverse transfer from vapour into solid is equal.

Equilibrium involving dissolution of solid or gases in liquids.
For dissolution of solid in liquids.
The rate of dissolution of solid substance = rate of crystallization of solid substance.
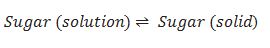
For dissolution of solid in liquids.

Define Henry’s Law.
The amount of solute that can be dissolved in given amount of solvent at given temperature in mole fraction is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas.
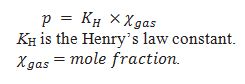
Define equilibrium/Dyanamic equilibrium.
Actual reaction doesn’t stop but it proceeds from both sides with same speed that is rate of forward reaction is equal to rate of backward reaction.
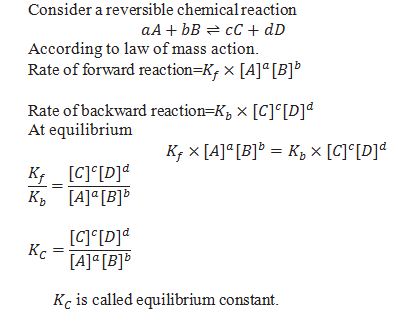
What is Law of mass action?
According to law of mass action rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of reactants raised to the power equal to stochiometric coefficient.
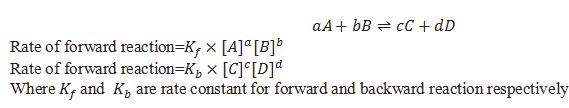
Equilibrium constant (Kc)
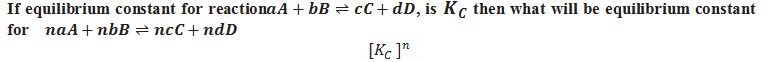
What is KP.
KP is equilibrium constant for reactions involving gaseous reactants and products. In place of concentration partial pressures are used.

What is the relationship between and KP and KC.
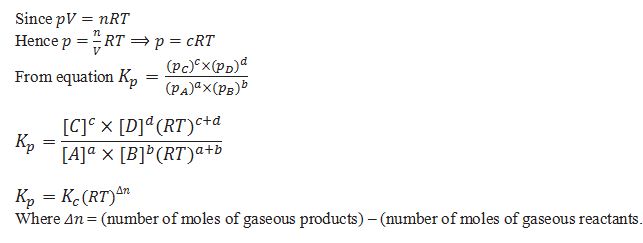
Define heterogeneous equilibrium reaction.
Reaction in which equilibrium exists between reactants and products having more than one phase is called heterogeneous equilibrium.
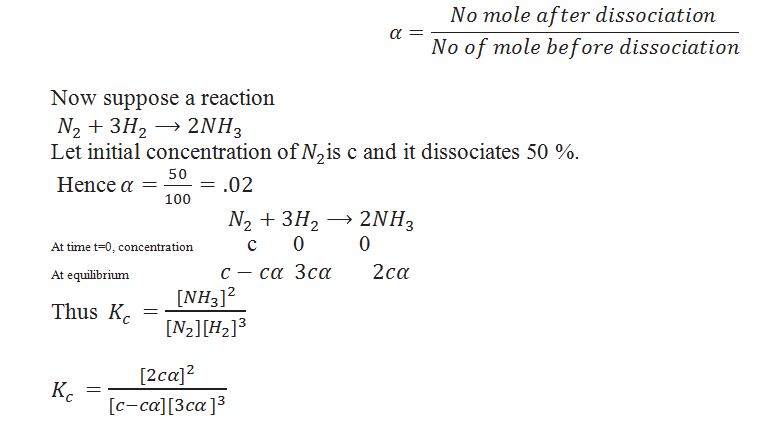
What is the significance of degree of dissociation![]() while calculating equilibrium constant KC
while calculating equilibrium constant KC
Factors effecting equilibrium constant.
(i) Equilibrium constant is independent of initial concentrations of the reactants and products.
(ii) Equilibrium constant depends on temperature only.
How can we predict the extent of reaction by using equilibrium constant.
(i) If value of Kc is very large that is greater than 103 than, the reaction is nearly to completion. The concentration of products is much larger than that of the reactants at equilibrium.
(ii) If value of Kc is very small that is lesser than 10-3 than, the backward reaction is favored. Concentration of reactants is much larger than that of products that is the reaction proceeds to a very small extent in forward reaction
(iii) If value of Kc is in between 103 and 10-3 than reaction proceeds toward equilibrium that is the reactants and products are comparable.
Define reaction quotient, Qc or Qp.
Reaction quotient is calculated similar as equilibrium constant but concentration of reactants and products are not necessarily equilibrium values.
How can we predict the direction of reaction by using reaction quotient.
(i) If Qc > Kc, the reaction is in reverse direction.
(ii) If Qc < Kc, the reaction is in forward direction
(iii) If Qc = Kc, the reaction mixture is at equilibrium.
When the particular reaction is non spontaneous, spontaneous and equilibrium
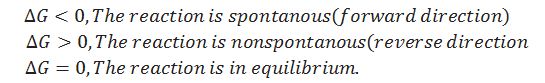
Define Le Chatelier’s principle.
According to this principle when a chemical equilibrium is disturbed by a change of temperature,pressure, concentration or presence of catalyst equilibrium shifts in that direction in which these changes can be nullified.
(i)Effect of concentration.
(a)Addition of reactant shifts the equilibrium in forward direction
(b)Addition of products shifts the equilibrium in backward direction.
(c)Removal of reactant shifts the equilibrium in backward direction.
(d)Removal of products shifts the equilibrium in forward direction.
(ii)Effect of temperature:
(a)Increase the temperature to an exothermic reaction shifts the equilibrium on backward direction.
(b)Increase the temperature to an endothermic reaction shifts the equilibrium on forward direction.
(iii)Effect of pressure:
Increase the pressure shifts the equilibrium in that direction in which lower number of moles of gaseous reactants or products are present.
(iv) Effect of catalyst:
Catalyst does not affect the equilibrium but it helps the reaction to achieve equilibrium faster.
What is electrolyte?
Substances which dissociates into constitutes cation and anion in aq. solution is called electrolyte.
Define the types of electrolyte.
There are two types of electrolytes strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte.
Strong electrolyte:Types of electrolyte which dissociates almost completely.
Examples: All salts(sodium chloride), Strong acids HCl,HNO3, H2SO4,H3PO4 ,HClO4,HBr,HI. Strong bases-Group 1 and group 2 elements hydroxides. Like NaOH,LiOH,KOH etc.
Weak electrolytes : Types of electrolyte which does not dissociates completely.
Examples:Weak acids like acetic acid,HNO2,HF etc. Weak bases like NH4OH.
Condition in which ionic equilibrium condition is established.
Ionic equilibrium condition is established in case of weak electrolyte, between dissociated ions and the unionized ions.
Define acids and bases according to Arrhenius theory.
Acids are substances which give H+( hydrogen ions) in water. and bases are substances that give OH– ( hydroxide ions) in water

What is the limitation of Arrhenius concept of acids and bases.
(i) Arrhenius concept is limited to only aq. Solution.
(ii) It does not explain the acidity and basicity of those compounds which do not contain hydrogen H+ and OH–.
What are the Bronsted and Lowry concept of acids and bases.
Acids are the substance which donate proton(H+) and bases the substance which accept proton.
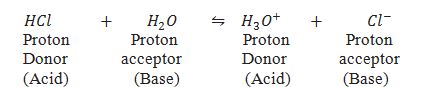
Define conjugate acid and base pairs.
The acid-base pair differs only by a proton(H+) is called a conjugate acid-base pair.
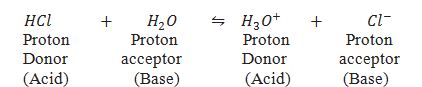
HCl and Cl– are conjugate acid base pairs.Similarly H2O and H3O+ are another conjugate acid base pairs.
Lewis acids and bases
Species which accepts electron pair are called Lewis acids and which donates an electron pair are called Lewis bases. Strong acids have weak conjugate bases and vice versa.
Examples of Lewis acids.
(i) Some +ve charge species are Lewis acids.
Like H+,Fe3+ etc.
(ii) Electron deficient molecules are Lewis acids.
Like BF3,AlCl3 etc.
Examples of Lewis bases.
(i)-ve charge species are Lewis bases
Cl–,OH– etc.
(ii) Electron rich molecules are Lewis bases.
Like H2O,NH3 etc.
Give Two reactions to prove amphoteric nature of water.
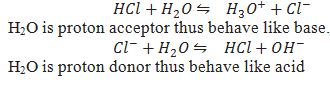
Pure water also show amphoteric behaviour how?
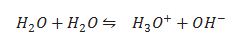
Ionic product of water.
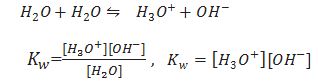
Because concentration of water (55.55 M) is very high and doesn’t change during reaction
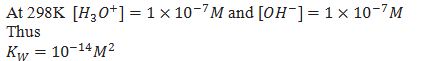
How can we determine the acidic, basic and neutral aq solution
[H3O+] > [OH– ]= Acidic
[H3O+] = [OH– ]= Neutral
[H3O+] < [OH–]= Basic
Define pH scale.

Prove pH+ pOH= 14
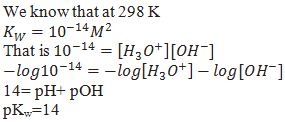
Ionization constant (Ka) for weak acid.

Ionization constant (Kb) for weak base
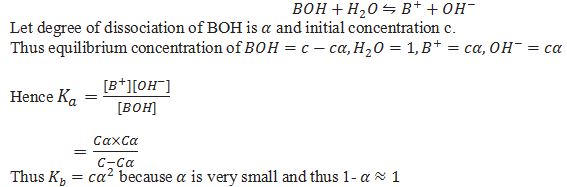
What is pKa and pKb.
pKa=-log[Ka] and pKb=-[log Kb]
Relation between Ka and Kb for conjugate acid base pair.
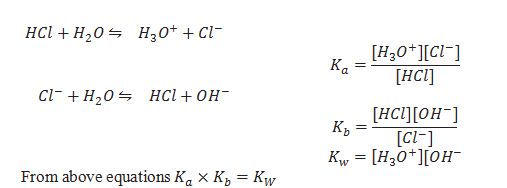
Determine the factors effecting acidic strength.
(i)Larger the value of ionization constant Ka higher the acidic strength.
(ii) In a given group acidic strength increases as the bond length increases.
Example: HI>HBr>HCl>HF
(iii) If the difference between electronegativity increases acidic strength increases.
Example: CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF
What is common ion effect.
Common Ion effect is based on the Le Chatelier’s principle. If any common ion is added equilibrium shifts in that direction in which this increased concentration is consumed.
What is difference between hydration and hydrolysis of salt?
Salt is dissociated into constituent ions in aq.solution and remains as hydrated ions called hydration.

When ions interact with water to form corresponding acids or bases called hydrolysis.
Examples:
(i) Salts of weak acid and strong base e.g.CH3COONa.
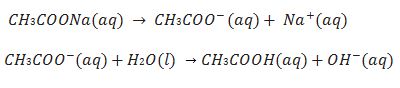
(ii) Salts of strong acid and weak base e.g. NH4Cl
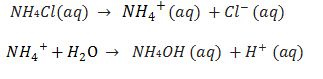
(iii) salts of weak acid and weak base, e.g.CH3COONH4

What is the formula for determining pH of aq.solution containing salt of weak acid and weak base, e.g.CH3COONH4
pH = 7 + ½ (pKa – pKb)
Define Buffer Solutions.
The solutions which resist change in pH value on the addition of small amounts of acid or alkali are called Buffer Solutions.
What is solubility product Ksp.
Equilibrium is established between the undissolved sparingly soluble salt in water
and the ions in a saturated solution.

