Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Define chemical bond.
The attractive force of attraction which holds the atoms together in a molecule called chemical bond.
What is octet rule?
Atoms can combine either by transfer of valance electrons from one atom to another or by sharing of valance electrons in order to have an octet in their valance shell.
How does ionic bond form explain with example?
Ionic bond forms by transfer of valance electron from one atom to another.
Example:Formation of NaCl
![]()
(i)Loss of an electron by Na metal and formation of cations.
![]()
(ii) Gain of an electron by Cl nonmetal and formation of anions
(iii)The negative anion and positive cation forms NaCl by electrostatic force of attraction.
Define electrovalent bond.
The electrostatic force of attraction between cation and anion which holds the ion together in a molecule is called electrovalent bond.
Define electrovalency.
The number of electrons loss or gain by elements in particular ionic compound is called electrovalency.
Example:NaCl
Electrovalencey of Na =1
Electrovalencey of Cl =1
Explain formation of covalent bond with example.
Covalent bond forms by sharing of electrons between two atoms.
Example formation of H2O.
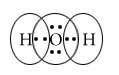
Define covalency.
Number of electrons an atom can share with other atoms is called covalency.
Example: In H2O Covalency of H=1,and covalency of oxygen is 2
The drawback of octet theory.
(i) Octet rule is based upon the chemical interest of noble gases .However some noble gases also form some compound.
(ii)Octet rule does not explain the shape of the molecules.
(iii) It does not explain the relative stability of the molecules.
Describe the factors for formation of ionic compound.
(i) Metals which form cation must have low ionization enthalpy.
(ii)Non metals which form anion must have high electron gain enthalpy.
(iii)Lattice enthalpy of ionic compound should be high.
Define lattice enthalpy.
Energy require to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into gaseous constituent ions is called lattice enthalpy.
Define bond order.
Number of bonds between two atoms in a molecule is called bond order.
Define bond length.
Bond length is defined as the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule.
Define covalent radius.
The covalent radius is half of the distance between two similar atoms joined by a covalent bond in a same molecule.
Define van der Waals radius.
Half of the distance between two similar atoms in a separate molecule.
Define bond angle.
Angle between the orbitals containing bonding electron pairs around the central atom in molecule.
Define Bond enthalpy.
Energy required to break one mole of bonds of a particular type between two atoms in a gaseous state.
Define average bond enthalpy.
Average bond enthalpy in a polyatomic molecule can be obtained by dividing total bond dissociation enthalpy by number of bonds broken.
Explain formal charge.
Formal charge =[Total number of valence electrons in the free atom]-[Total number of nonbonding electrons( lone pair electrons)]-1/2[Total number of bonding (shared electrons) electrons]
What are the limitations of octet rule?
(i)The incomplete octet of the central atom.
(ii )Odd –electron molecules.

(iii)The expanded octet

Draw Lewis dot structure of following compound.
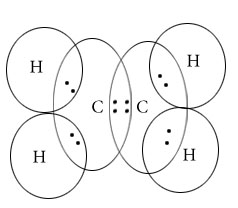
C2H4
N2

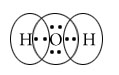
H2

O2
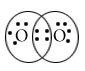
O3

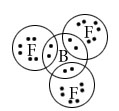
NF3

CO32-
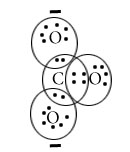
H2O
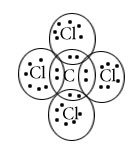
CCl4
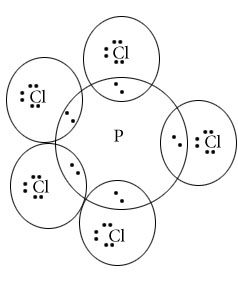
PCl5
SF6

H2SO4
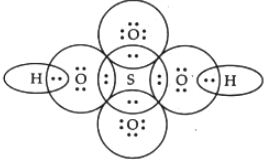
CH4

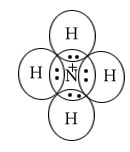
NH4+
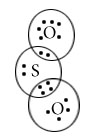
SO2
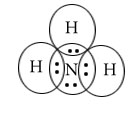
NH3
SF4
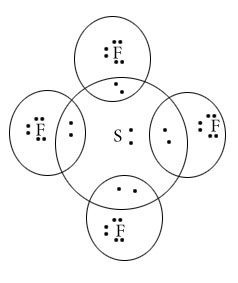
ClF3
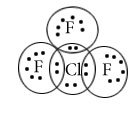
BrF5

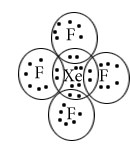
XeF4
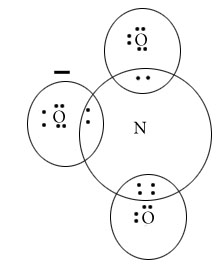
NO3 –
What is Fajan’s Rule?
The partial covalent character of ionic bond was discussed by Fajan’s,by following rules.
(i)The smaller the size of cation and the larger the size of anion the greater the covalent character of particular ionic bond.
(ii)The greater the charge on the cation the greater the covalent character if the ionic bond.
Explain VBT with example.
(i)Covalent bond between two atom forms by overlapping of atomic orbitals.
(ii)Only valence shell orbitals can take part in bonding and must have opposite spin.
(iii)Greater the overlap the stronger is the bond formed between two atoms.
Example : Formation of H2 molecule.
H2
Electronic configuration of one H atom 1s1 
Shape of s orbital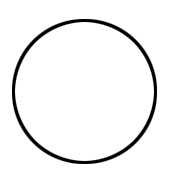
Overlapping
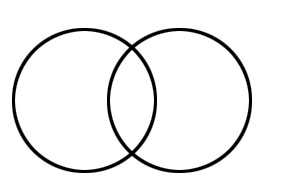
Thus H-H forms, having one bond
Explain the formation of following molecules on the basis of VBT.
N2
Electronic configuration of one N atom 1s2,2s2,2p3
Shape of three p orbitals
Overlapping
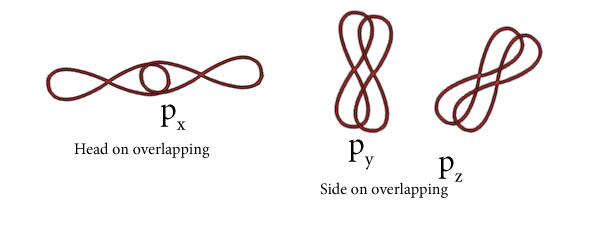
O2
Electronic configuration of one O atom 1s2,2s2,2p4
Shape of two p orbitals
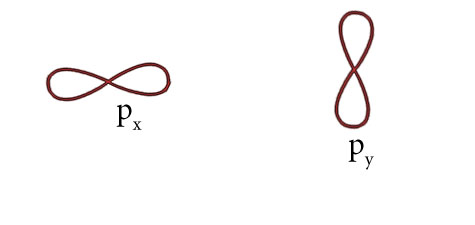
Overlapping
Thus O=O forms having one sigma and one pi bond.
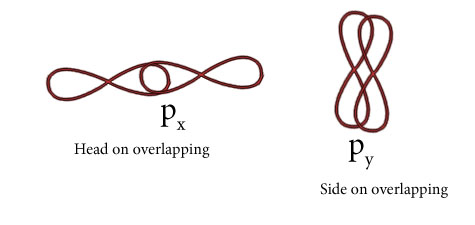
Mention two types of overlapping and nature of covalent bond.
There are two types of bond formed during overlapping of atomic orbitals.
(i)Sigma bond( Covalent bond which forms by head on overlapping along the intermolecular axis.
Following types of overlapping can form sigma bond
(i)s-s overlapping.
(ii)s-p overlapping.
(iii)p-p overlapping.
(iii )Pi Bond( Covalent bond forms by side on overlapping .
Following types of overlapping can form pi bond.
(iii)p-p overlapping.
Which bond is stronger in sigma and Pi bond?
Sigma bond is stronger bond than Pi bond because in case of sigma bond the overlapping of orbitals takes place to a larger extent.
What are the main postulates of VSEPR theory.
(i) Electron pair Geometry of the molecule is decided by both bond pair and lone pair orbitals ,but Molecular geometry of the molecules is decided by only bond pair orbitals.
(iii)The repulsive interaction of electrons pair decreases in the following order.
Lone pair(lp)-lone pair(lp) > Lone pair(lp)-bond pair(bp) > bond pair(bp)-bond pair(bp)
What are the steps to find shape of the molecules according to VSEPR theory.
Example: NH3
Step (i)Write Lewis dot structure of NH3.
Step(ii)Chose central atom here it is N
Step(iii)Find bond pair orbitals and lone pair orbitals
bp=3,lp=1
Step(iv)Find the sum of lp and bp
Here lp+bp=4
Now structure is determined by following table.
| lp+bp | Structure (Electron pair Geometry) |
| 2 | Linear |
| 3 | Trigonal planer |
| 4 | Tetrahedral |
| 5 | Triangular bipyrmidal |
| 6 | Square bipyramidal |
| 7 | Pentagonal bipyarnidal |
Determine the shape of following molecules.
NH3

Central atom=N
l.p=1
b.p=3
l.p+b.p =4
Electron pair Geometry=Tetrahedral

Molecular Geometry= Pyramidal
H2O
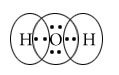
Central atom=O
l.p=2
b.p=2
l.p+b.p =4
Electron pair Geometry=Tetrahedral

Molecular Geometry=Bent/Angular
CCl4

Central atom=c
l.p=0
b.p=4
l.p+b.p =4
Electron pair Geometry/Molecular Geometry =Tetrahedral
BeH2
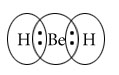
Central atom=Be
l.p=0
b.p=2
l.p+b.p =2
Electron pair Geometry /Molecular Geometry=Linear
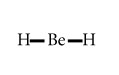
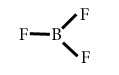
BF3

Central atom=B
l.p=0
b.p=3
l.p+b.p =3
Electron pair Geometry/Molecular geometry=Trigonal planer
PF5
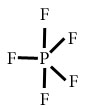
Central atom=P
l.p=O
b.p=5
l.p+b.p =5
Electron pair Geometry/Molecular geometry=Trigonal bipyramidal
SF6

Central atom=S
l.p=0
b.p=6
l.p+b.p =6
Electron pair Geometry/Molecular geometry=Square bipyramidal
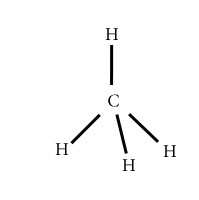
CH4

Central atom=C
l.p=O
b.p=4
l.p+b.p =4
Electron pair Geometry/Molecular geometry=Tetrahedral
SF4

Central atom=S
l.p=1
b.p=4
l.p+b.p =5
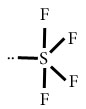
Electron pair Geometry=Trigonal bipyramidal
Molecular geometry=See-Saw
ClF3
Central atom=Cl
l.p=2
b.p=3
l.p+b.p =5
Electron pair geometry=Trigonal bipyramidal

Molecular Geometry=T shape
XeF4

Central atom=Xe
l.p=2
b.p=4
l.p+b.p =6

Structure=Square bipyramidal
Shape-Square Planar
Define Dipole moment.
The Product of the magnitude of charge and the distance between the centers of the two positive and negative and nonpolar covalent co charge is called dipole moment.
What is Debye(D)
Debye is unit of dipole moment.
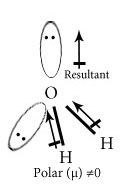
What is polar covalent compound and nonpolar covalent compound?
Polar covalent Compound-Compounds having net dipole moment not equal to zero are polar covalent compound.
Non polar covalent Compound-Compounds having net dipole moment equal to zero are nonpolar covalent compound
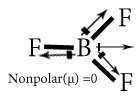
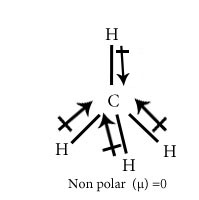
Chose the polar and nonpolar compound in following compounds.
NF3
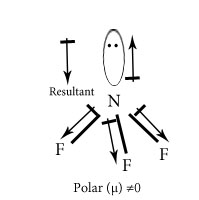
H2O
BeF2
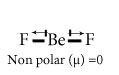
BF3
CH4
NH3

In NH3 and NF3 which has higher dipole moment?
 |
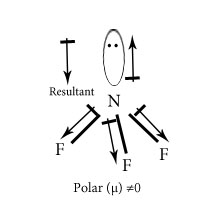 |
Dipole moment of NH3 is higher than that of NF3. In NH3 the orbital dipole due to lone pair is in same direction as the resultant dipole moment of N-H bonds ,whereas in NF3 the orbital dipole is in the direction opposite to the resultant dipole moment of three N-F bonds.
Explain the term resonance in a covalent compound.
When a particular compound can be draw in more than two Lewis dot structure in which atomic positions are remain constant and differ on only arrangement of electrons.
Draw the resonating structure of following compounds.
CO2
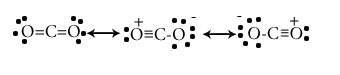
O3
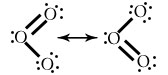
SO3
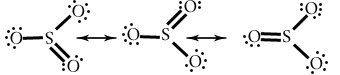
NO3–

CO32-

Define hybridisation.
The process of intermixing of the orbitals having slightly different energies and formation of new type of orbitals called hybrid orbitals of equivalent energies and shape.
What are the different types of hybridization and their structures.
| Hybridisation | Structure |
| sp | Linear |
| Sp2 | Triagonal planer |
| Sp3 | Tetrahedreal |
| Sp3d | Triangular bipyramidal |
| Sp3d2 | Square bipyramidal |
Using hybridization theory show the formation of following molecules.
H2O
Central atom is Oxygen
Electronic configuration in ground state
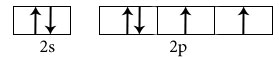
Hybridisation among 2s and 2p orbitals
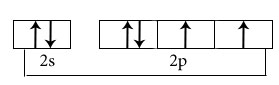
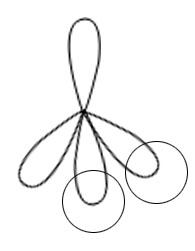
Hybridisation is sp3
Orientation of four sp3 hybrid orbitals in space
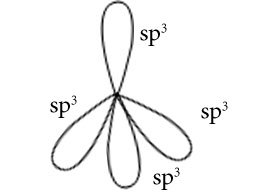
Overlapping between hybrid orbital and s orbital of hydrogen and formation of two bonds.
BCl3
Central atom is B
Electronic configuration in ground state

Electronic configuration in excited state
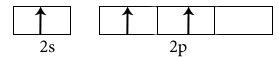
Hybridisation among 2s and 2p orbitals
Hybridisation is sp2
Orientation of three sp2 hybrid orbitals in space
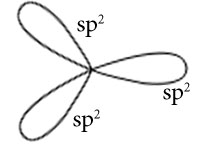
Overlapping between hybrid orbital and p orbital of Chlorine and formation of three bonds.
PCl5
Central atom is P
Electronic configuration in ground state

Electronic configuration in excited state

Hybridisation among 3s ,3p and 3d orbitals

Orientation of five sp3d hybrid orbitals in space

Overlapping between hybrid orbital and p orbitals of chlorine and formation of five bonds.
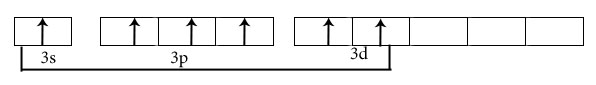
SF6
Central atom is S
Electronic configuration in ground state

Electronic configuration in excited state

Hybridisation among 3s ,3p and 3d orbitals
Orientation of five sp3d2 hybrid orbitals in space

Overlapping between hybrid orbital and p orbitals of fluorine and formation of six bonds.
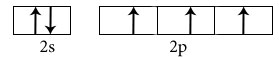
CH4
Central atom is Carbon
Electronic configuration in ground state
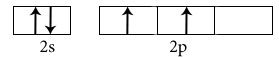
Electronic configuration in excited state
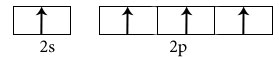
Hybridisation among 2s and 2p orbitals
Hybridisation is sp3
Orientation of four sp3 hybrid orbitals in space

Overlapping between hybrid orbital and s orbitals of hydrogen and formation of four bonds.

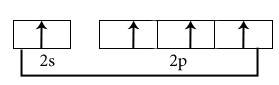
NH3
Central atom is N
Electronic configuration in ground state
Hybridisation among 2s and 2p orbitals
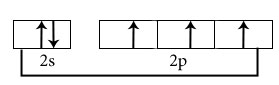
Hybridisation is sp3
Orientation of four sp3 hybrid orbitals in space

Overlapping between hybrid orbital and s orbitals of hydrogen and formation of three bonds.

C2H4
Central atoms are two carbon atoms.
Electronic configuration in ground state
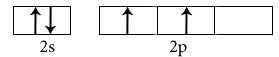
Electronic configuration in excited state
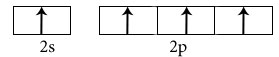
Hybridisation among 2s and 2p orbitals
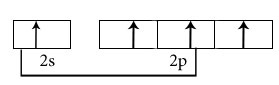
Hybridisation is sp2
Orientation of three sp2 hybrid orbitals in space
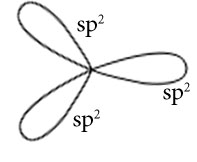
Similarly of other carbon atoms
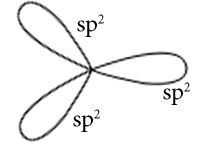
Overlapping

C2H2
Central atoms are two carbon atoms.
Electronic configuration in ground state

Electronic configuration in excited state

Hybridisation among 2s and 2p orbitals
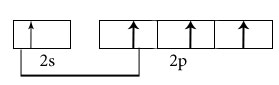
Hybridisation is sp
Orientation of two sp hybrid orbitals in space
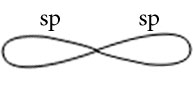
Similarly of other carbon atoms
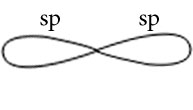
Overlapping
What are the main features of molecular orbital theory?
(i)Like atoms are present in the atomic orbitals ,electrons in a molecule are present in a molecular orbitals.
(ii)The atomic orbitals of proper orientation combine to form molecular orbitals.
(iii)Like electron in a atomic orbitals are influenced by one nucleus ,in molecular orbital it is influenced by two or more nuclei.
(iv)The number of molecular orbitals formed are equal to the number of combining orbitals half are called bonding orbitals and another half are called antibonding orbitals.
(v)Bonding molecular orbitals have greater stability because they have lower energy than that of antibonding orbitals.
(vi)Molecualr orbitals are filled according to the aufbau principle,Pauli’s ,Hund’s rule.
What is LACO theory.?
LCAO-linear combination of atomic orbitals.
Let a molecule contain two atoms A and B .Formation of molecular orbitals are due to linear combination of atomic orbitals that can take place by addition and by subtraction of wave functions.
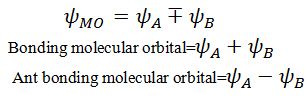

What is the sequence of energy levels of molecular orbitals.

Define bond order.
Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in bonding and antibonding orbitals.
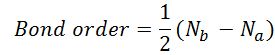
Explain stability of compound using bond order.
Stable molecule-Nb>Na
Unstable molecule- Nb<Na, Nb=Na
When is compound diamagnetic and paramagnetic?
(i)If all the molecular orbitals in a molecule are doubly occupied the substance is diamagnetic and repelled by magnetic field.
(ii) If one or more molecular orbitals are singly occupied the substance is paramagnetic and attracted by magnetic field.
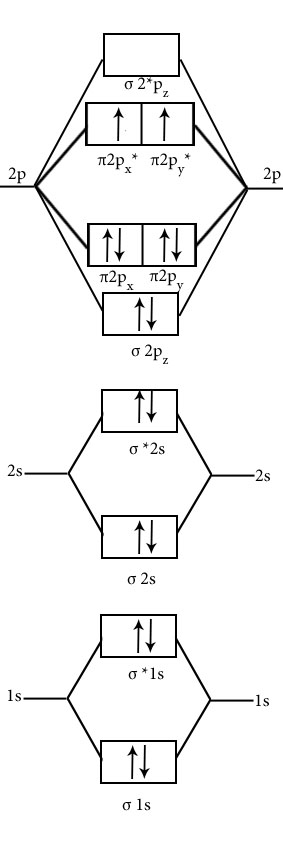
Discuss the bonding of H2, He2, Li2, C2, O2 O2+,O2– on MOT




Draw molecular orbital diagram of ,H2,He2,O2.
H2
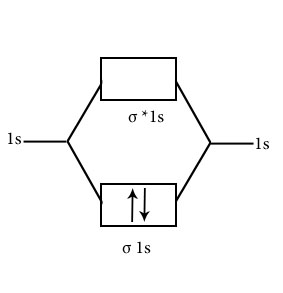
He2
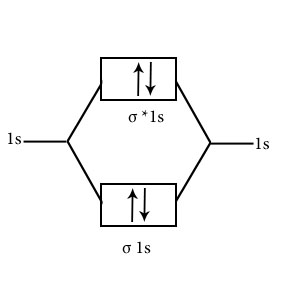
O2
Define H-bonding.
The attractive force which binds hydrogen atom of one molecule with the F,O,N of another molecule.
Define the two types of H-bonding.
(a)Intermolecular H-bonding.
(b)Intramolecular H-bonding.
(a)Intermolecular H-bonding.
It forms between two different molecules of the same or different compounds.
Example:H-F.H2O etc
(b)Intramolecular H-bonding.
It forms when H-atom and F,O,N is present on the same molecule.
Example :O-nItrophenol.
