Classification of elements and periodicity in properties
Why do you need to classify elements?
It is very difficult to study chemistry of all elements individually ,because number of elements are very large.
Explain Dobereiner ‘s triads rule.
Dobereiner arranged three elements in increasing order of their atomic weight called triads ,He observed that the middle elements of each triads had an atomic weight equal to the arithmetic mean of the other two.
Example.Li(7) ,Na(23),K(39)
What was the major drawback of Dobereiner ‘s triads rule?
The triads rule valid for limited number of elements.
Explain Newlands Law of octaves.
He arranged the elements in increasing order of their atomic weights and noticed that every eight element have properties similar to the first element.
What was the major drawback of Newland’s octave rule?
The Law was true only for elements up to Ca.
Explain Mendeleev periodic law.
The properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic weight.
What was the major drawback of Mendeleev periodic table?
Iodine with lower atomic weight than that of tellurium was placed in group VII along with F,Cl.Br.I.
Give special property of Mendeleev periodic table which makes it very special.
He proposed that some of the elements were still discovered and left the several gaps in the table. For example both Galium and Germaimum were unknown at the time Mendeleev published his periodic table. He left the gap under Al and Si and called these elements Eka Aluminium and Eka silicon.
What do you mean by Eka Aluminium and Eka silicon?
He left the gap under Al and Si and called these elements Eka Aluminium(Galium) and Eka silicon(Germanium).
What is modern periodic law?
The properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic number.
What do you mean by periods and groups in long form of periodic table.
The Horizontal rows are called periods and vertical columns are called groups.
How many groups and periods are in long form of periodic table?
There are eighteen groups (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18) and seven periods (1,2,3,4,5,6,7)
What is the IUPAC name of elements having atomic number 101 and 102?
101-Unnilunbium.
102-unnilnium.
4f and 5f inner transition series of elements are placed in the separately in the periodic table why?
To maintain the structure and preserve the principle of classification by keeping elements with similar properties in a single column.
Why the elements of same group exhibit similar chemical behavior?
Because these elements have the same distribution of electrons in their outermost shell.
Long form of periodic table is classified into four blocks name that groups.
1.S-block elements.
2.p-block elements.
3.d-block elements.
4.f-block elements.
What is the general electronic configuration of the last shell of
1.S-block elements 2.p-block elements 3.d-block elements 4.f-block elements.
1.S-block elements-[ns1-2]
2.p-block elements-[ns1-2np1-6]
3.d-block elements[(n-1)d1-10ns0-2]
4.f-block elements[(n-2)f1-14(n-1)d0-1ns2]
Define following terms.
1.Alkali metals.2.Alakaline earth metals.3.Representative elements or Main group elements.4.Noble gases.5.Halogens.6.Chalogens.7.Transition elements.8.inner transition elements.
1.Alkali metals.-Group 1 elements.
2.Alakaline earth metals. Group 2 metals.
3.Representative elements or Main group elements.-S-block elements and p-block elements.
4.Noble gases.Group 18 elements.
5.Halogens-Group 17 elements.
6.Chalogens-Group 16 elements.
7.Transition elements-d-block elements.
8.inner transition elements-f-block elements.
Why are group 1 elements called alkali metals?
When alkali metals are dissolved in water they form hydroxide which are basic in nature.
Why are group 2 elements called alkaline earth metals.
Hydroxide and oxide of group 2 elements are basic in nature and they are found in earth crust.
Group 18 elements are called Noble gases why?
All the orbitals in the valence shell of the Noble gases are completely filled by electrons and it is very difficult to remove electrons.
d-block elements are called Transition metals why?
d-block elements forma bridge between the chemically active metals of s-block elements and less reactive elements of group 13 and group 14.
What are Lanthanoids and Actinoids.
Lanthanoids-14 elements after La are called Lanthanoids.Last electron goes into 4f orbital.
Electronic configuration is 4f1-145d0-16s2.
Actinoids. 14 elements after Ac are called Actinoids.Last electron goes into 5f orbital.
Electronic configuration is 5f1-146d0-17s2.
What are transuranium elements?
The elements after Uranium are called transuranium elements.
Properties of s-block elements.
1.s-block elements are metals.
2.They are high reactive metals.
3.They have low ionization energy.
4.They lose the outermost electrons readily to form +1 ions(Group 1 elements)+and +2 ion (group2 elements.)
5.The compounds of the s-block elements are ionic except Li and Be.
Properties of the p-block elements.
1.p-block elements contain both metals and non metals.
2.Group 17 and group 16 elements are mainly nonmetals.
3.Group 17 and and Group 16 elements have very high negative electron gain enthalpy.
4.Group 18 elements are noble gases.
Properties of d-block elements.
1.They all are metals.
2.They form colored ions .
3.They have variable oxidation states.
4.They are paramagnetic.
5.They are good catalyst.
Zn,Hg,Cd do not show most of the properties of transition metals due to completely filled d –orbitals.
Properties of f-block elements.
1.They all are metals.
2.With in each series properties of the elements are quite similar.
3.The chemistry of actinoids are more complicated than the corresponding lanthanoids.
4.Actionoids are radioactive elements.
How many types of elements are in periodic table.
There are two types of elements.
1. Metals-78% of all elements are metals. They are located in left side of periodic table.
2. Non metals. They are located in at the top right side of the periodic table.
What are the properties of metals?
1.Metals are usually solid at room temperature.
2.They are good conductors.
3.They have high melting and boiling point.
4.They are malleable and ductile.
What are the properties of non metals?
1.Usually solids or gas at room temperature.
2.Low melting point and boiling point.
Boron and carbons are exceptions.
3.They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
4.Brittle and are neither malleable and ductile.
5.Metallic character increases top to bottom and decreases left to right.
6.Non metallic decreases top to bottom and increases left to right.
What are semi metals and metalloids?
Elements which show properties of both metals and non metals.
eg. Silicon ,Germanium,Arsenic ,Antimony and Tellurium.
What do you mean by covalent radius and metallic radius.
Covalent radius-It gives the size of an atom of non metal. It is the half of the distance between two atoms when they are bound together by a single bond.
Metallic radius-Half of the distance between two adjacent kernels present at the lattice site in crystal.
Atomic size of elements increases top to bottom why?
As we go down the group number of shell per period increases thus size increases.
Atomic size of elements decreases from left to right in period why?
As we go from left to right in period shell number remains constant and electrons are added to same shell thus attraction between nucleus and outermost electron increases thus size decreases.
The size of anion is larger than its parent atom why?
It is due to addition of one or more electron would result in increased repulsion among the electrons and decrease in effective nuclear charge.
The size of cation is smaller than its parent atom why?
It is due to removal of one or more electron would result in decreased repulsion among the electrons and increases in effective nuclear charge.
The cation with the greater positive charge will have a smaller radius why?
It is due to greater attraction of the electron to the nucleus.
The anion with the greater –ve charge will have large radius why?
It is due to the net repulsion of the electron will more outweigh the nuclear charge and the will expand in size.
Define ionization enthalpy.
The energy required to the remove an electron from an isolated gaseous atom.
Define first Ionization enthalpy and second ionization enthalpy.
The first ionization enthalpy for an element X is the enthalpy change for the reaction.

The second ionization enthalpy for an elements X is the enthalpy change for the reaction.

Why Ionization enthalpies are always positive?
Because energy is always required to remove electron from an atom.
Why second ionization is always higher than the first ionization enthalpy.
It is more difficult to remove an electron from an positively charged ion than from neutral atom.
What is shielding effect or screening effect?
The effective nuclear charge experienced by an valance electron in an atom will be less than the actual charge on nucleus because of the repulsion between the core electrons and valance electrons.
Why 1st ionization enthalpy of elements decreases top to bottom in group why?
It is due to atomic size increases top to bottom in group.
Ionization enthalpy of elements increases in period from left to right why?
Atomic size of elements decreases from left to right in period.
The first ionization enthalpy of boron(B) is slightly higher than Beryllium(Be) why?
In Be electron is removed from fully filled (stable) 2s orbital and in boron the electron is removed from partially filled(less stable) 2p orbital.
The 1st ionization enthalpy of oxygen (o) is lower than that of Nitrogen(N) why?
It is easier to remove a electron from partially filled (2p4)orbital in case of oxygen than that of half orbital (2p3) orbital in case of nitrogen.
What are isoelectronic species?
Atoms and ions which contain the same number of electron is called isoelectronic dpecies.
e.g.O2- =10 electron.F–=10 electron.
Elctron gain enthalpy increases from left to right up to group 17 why?
It is due to the size of atom decreases from left to right in period.
Why negative electron gain enthalpy decreases from top to bottom in group why?
It is due to the size of atom increases from top to bottom in group.
Which oxidation state is shown by group 1 and group 2 elements?
Group 1 elements have only one valance electron hence they show +1 oxidation state Group 2 elements have two valance electron hence they show +2 oxidation state .
Periods 2 elements (top elements from group 13-17) show anomalous behavior why?
I t is due to small size ,high electronegativity and unavailability of d orbitals.
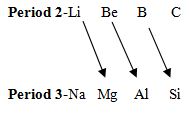
What do you mean by diagonal relationship?
Properties of 2 elements are similar with properties of period 3 elements diagonally.
The 1st member of group 13-17 show anomalous behavior why?
1st member of group has only four valance orbitals one 2s and three 2p orbitals ,whereas the other members have d orbitals hence they can expand their covalency.
B can only form BF4– whereas Al Can form AlF63- why?
It has due to B has only four valance orbitals but Al has d-orbitals thus it can expand its covalency.
The first member of p-block elements display greater ability to form multiple bonds to itself and to the other elements (like C=C,C=N,N=O) but other elements not why?
It is due to first member of p-block element has following properties.
1.Small size.
2.large charge/radius ratio.
3.High electronegativity.
Group 1 elements and halogens are highly reactive why?
Group1 elements have only one valance electron on their last shell hence they can lose electron easily and thus can form cation easily.
Halogens are seven electron on their last shell hence they need only on electron to complete their octet thus can form anion easily.
